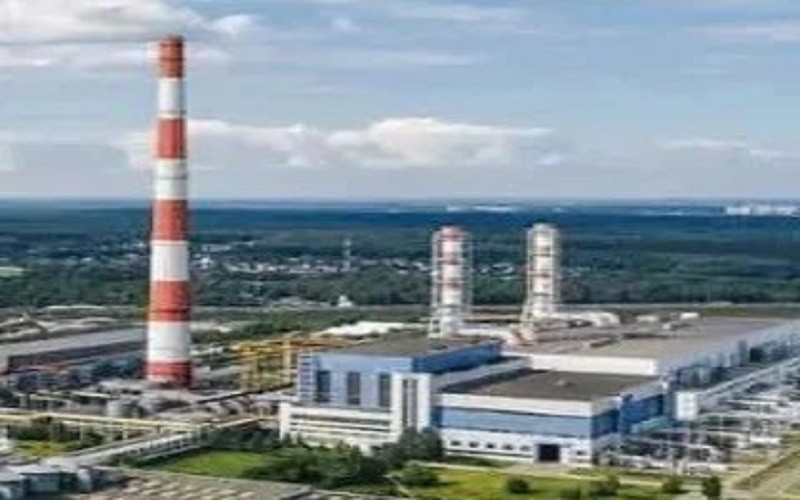
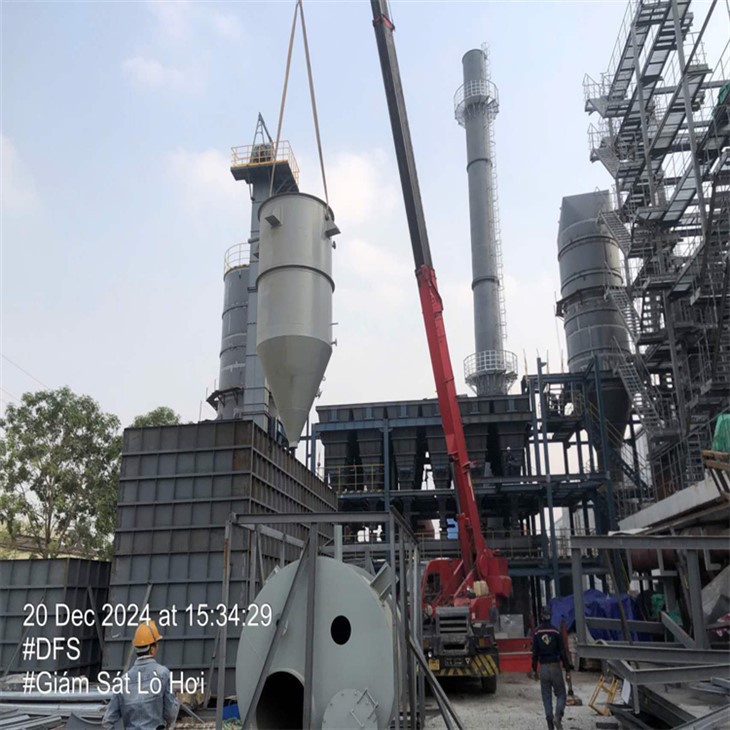
Waste incineration is simply the burning of garbage. The incineration process, often described in the industry as thermal treatment, uses special incinerators that burn waste materials to ash, heat, and flue gas (i.e., gas exiting from a flue, such as a chimney, to the surrounding air).
Benefits of Solid Waste Incinerator
Reduces the volume of solid waste
Incinerators can reduce the volume of waste by about 95% and reduce the solid mass of the original waste by 80% to 85%. (The exact percentage depends on the materials that the solid waste is made of). Incineration doesn't completely eliminate the need for landfill space, but it can significantly reduce the space needed. This is especially important in urban areas, where there may be many other ways to use land more efficiently.
Sustainable energy
Solid waste can actually be converted into electricity. This process is called waste-to-energy incineration. In special facilities, non-hazardous waste can be burned in high-tech incinerators that convert the waste into electricity. This takes pressure off the grid by creating sustainable energy and saves space in landfills.
Helps reduce pollution
Studies have shown that solid waste incineration actually produces less pollution than landfills. One study in particular compared landfills and waste incineration facilities of the same size. The study found that the landfills tested actually released higher amounts of greenhouse gases, hydrocarbons, non-methane organic compounds, hazardous air pollutants, nitrogen oxides, and dioxins than the waste incineration facilities tested. Additionally, over time, landfills can contaminate groundwater systems by releasing hazardous chemicals into the groundwater through the surrounding soil.
Filters Capture Pollutants
One of the biggest concerns about waste incineration is that it releases dangerous toxins into the air, specifically compounds called dioxins. Fortunately, today's incineration facilities use highly specialized filters to capture harmful gases and particles like dioxins.
As the amount of waste generated by human activities continues to increase, it is becoming increasingly important to find effective and environmentally friendly solutions to deal with this waste. One widely adopted technology is the use of waste-to-energy plants, also known as waste-to-energy incinerators or waste-to-energy facilities.
Municipal Solid Waste Incinerator
Municipal solid waste incinerator is an effective way to handle the increasing amount of trash in urban areas. This type of incinerator is designed to burn solid waste, including household garbage, industrial waste, and medical waste. The goal is to reduce the volume of the waste by up to 90% and convert it into ash and gas emissions.
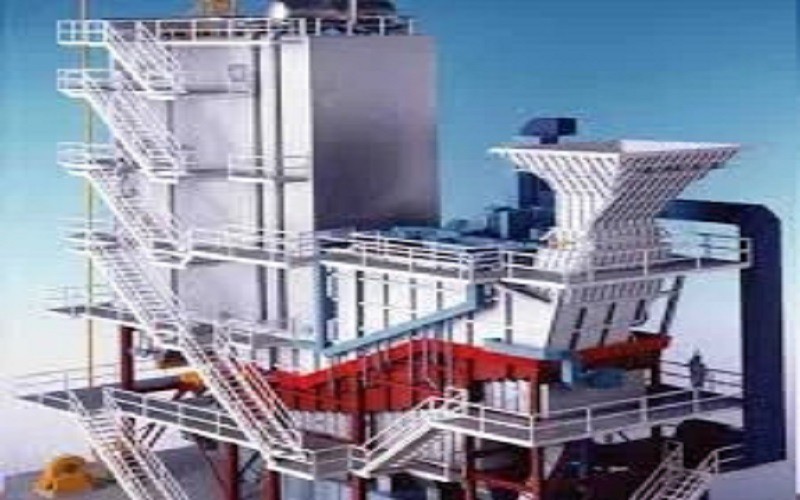
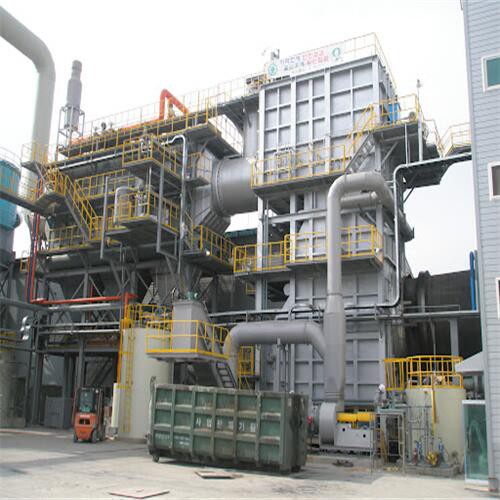
Tenor made small waste incineration system was developed by Tenor Low Carbon New Energy Technology (Liaoning) Co., Ltd. and Dalian University of Technology research team. WTE incineration system including hopper, feeding machine, stoker furnace, step grate, ash hopper, slag removal system, transport aircraft and combustion chamber, suitable for daily capacity of 50 to 250 tons/d of small domestic waste incineration projects.
Tenor made small waste incineration system was developed by Tenor Low Carbon New Energy Technology (Liaoning) Co., Ltd. and Dalian University of Technology research team. WTE incineration system including hopper, feeding machine, stoker furnace, step grate, ash hopper, slag removal system, transport aircraft and combustion chamber, suitable for daily capacity of 50 to 250 tons/d of small domestic waste incineration projects.
Tenor made small waste incineration system was developed by Tenor Low Carbon New Energy Technology (Liaoning) Co., Ltd. and Dalian University of Technology research team. WTE incineration system including hopper, feeding machine, stoker furnace,step grate, ash hopper, slag removal system, transport aircraft and combustion chamber, suitable for daily capacity of 50 to 250 tons/d of small domestic waste incineration projects.
We provide high -quality products, professional services, customized solutions.
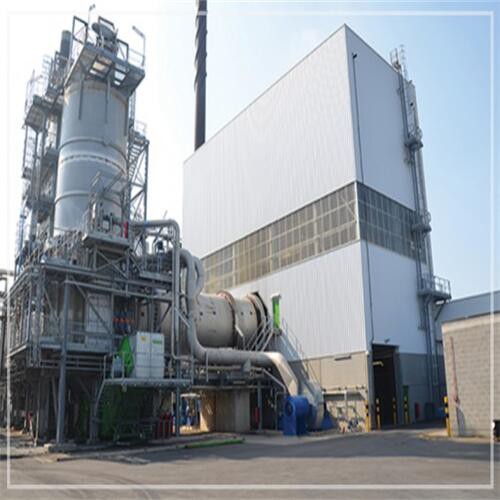
Our waste to energy incinerator is an advanced and eco-friendly solution for managing waste. With this incinerator, waste is converted to energy, reducing the amount of waste disposed in landfills and producing electricity or heat for various applications. Our incinerator features advanced technologies that ensure efficient and clean combustion, resulting in lower emissions and better air quality.
Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Plant
Our municipal solid waste incineration plant is a state-of-the-art facility designed to effectively and efficiently dispose of urban waste. With advanced technology and strict environmental standards, our plant can safely and sustainably handle large volumes of solid waste, while minimizing emissions and reducing landfill waste.
Why Choose Us
Advanced equipment
We take strong measures to ensure that we use the highest quality equipment in the industry and that our equipment is regularly and meticulously maintained.
Rich experience
Has a long-standing reputation in the industry, which makes it stand out from its competitors. With over many years of experience, they have developed the skills necessary to meet their clients' needs.
Efficient and convenient
The company has established marketing networks around the world to provide high-quality services to customers in an efficient and convenient manner.
Quality assurance
In terms of quality assurance, the company strictly follows the standards and norms of the industry quality system. Adopt industry-leading testing equipment to ensure product quality and good reputation.
Professional team
We have a team of skilled and experienced professionals who are well-versed in the latest technology and industry standards. Our team is dedicated to ensuring that our customers get the best service and support possible.
Competitive prices
We offer our products at competitive prices, making them affordable for our customers. We believe that high-quality products should not come at a premium, and we strive to make our products accessible to all.
Efficient Treatment of Municipal Solid Waste in Incinerators for Energy Production
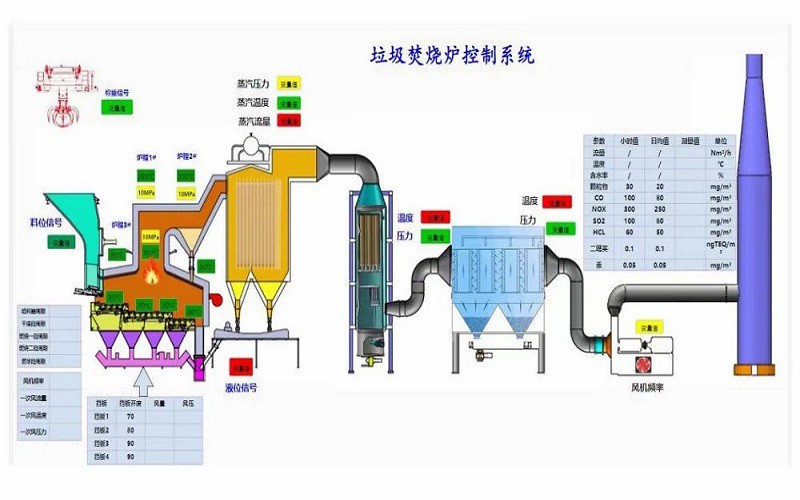
The generation of municipal solid waste has increased dramatically worldwide, exceeding the capacity of municipalities to handle it. Using incinerators to treat the waste and recover energy has been chosen as an environmentally friendly method of waste management. Waste incineration leads to inefficiencies in energy generation. Summarize the problems that lead to inefficient municipal solid waste treatment and the potential for improvement. High temperature corrosion and ash deposition on heat exchange surfaces are the main causes of inefficiency in waste incineration. Optimizing the operating conditions during the incineration process can reduce corrosion and ash deposition problems. The operating conditions can be optimized by performing kinetic modeling, which determines the conditions that reduce the corrosion rate. These conditions are moisture content ~10 vol.% and SO2 ~250 ppm. The use of eco-tubes and sergher boiler prisms ensures high turbulence and mixing within the boiler, which reduces ash problems and thus improves incineration efficiency. Sorting of MSW using a max Al robotic sorter and removal of alkaline chlorides from the waste using sink-float processes, centrifuges, and cyclone separation techniques reduce the chlorine load, which reduces severe ash problems and has been shown to be beneficial in improving the efficiency of incinerators for MSW treatment.
Waste Crane
A waste crane picks up massive loads of garbage from a sorted mound.
Throat
The throat is a large long tunnel that leads to the primary combustion chamber.
Primary Combustion Chamber
Waste from the throat goes to the main combustion chamber where the material is burned. Most often, this chamber is already hot thanks to the high ambient temperature that is constantly controlled and retained.
Secondary Chamber
The secondary chamber is often called the ''afterburner.'' Facilities in Europe, Australia, Canada, and the US are required by law to have an afterburner. This chamber helps reduce or prevent harmful particulates from forming by burning them off.
Many countries have laws that require all flue gas remain in the secondary chamber for at least 2 seconds at a temperature of 850 degrees Celsius to break down toxic organic substances.
Superheater
Using superheaters, heat from the flue gasses can be used to convert water to steam. The superheated steam can then be used to drive turbines to generate electric power in WTE facilities. The flue gas is now at 200 degrees Celsius at this point.
Flue Gas Cleaning System
Before exiting the facility, the flue gas goes through the cleaning system to purge acids, heavy metals, and other toxic particulates.
Flue Stack
Once the flue gas is treated, it exists through the flue stack, commonly called a chimney. Laws require a stack height of at least 3 meters for localized incinerators. Bigger ones, however, have multi-story chimneys, especially those that handle the massive trash produced by large cities. Also, chimneys may be built higher or lower than recommended due to various atmospheric conditions.
Burners
The flame coming from the burners ignites the garbage. The majority of the incinerators are equipped with low nitrous oxide burners or modulated gas flow burners. The intensity of the flames is carefully controlled.
Fuel tanks
Fuel tanks are used to store fuel. Fuel tanks must be carefully insulated for safety.
Ash pit
After incineration, the remnant ash is then collected in an ash pit for disposal. Some entities purchase the ash for their own use.
How to Choose a Garbage Incinerator
Determine the type of garbage incinerator. Choose the appropriate type of garbage incinerator according to the composition, processing volume, processing requirements and environmental protection requirements of the garbage. Common types of garbage incinerators include mechanical grate incinerators, fluidized bed incinerators, rotary kiln incinerators, etc. Different types of incinerators are suitable for different types of garbage, and their treatment effects and characteristics are also different.
Choose the appropriate processing volume Choose the appropriate garbage incinerator according to the processing volume of the garbage. If the garbage processing volume is large, you need to choose an incinerator with a stronger processing capacity; conversely, if the garbage processing volume is small, you can choose an incinerator with a smaller processing capacity.
Consider environmental protection performance The environmental protection performance of the garbage incinerator is one of the important factors in selection. A garbage incinerator that meets environmental protection standards, has low nitrogen oxide emissions, low smoke emissions, and low noise should be selected. At the same time, it is also necessary to consider its ability to handle odors and whether it is necessary to add combustion aids.
Examine the reliability of the equipment The garbage incinerator is a continuously operating equipment, and its reliability is crucial for garbage treatment. When choosing a waste incinerator, factors such as the life of its key components, maintenance, and safety protection should be considered to ensure its long-term stable operation.
Consider the energy consumption and operating cost of the equipment The operating cost of the waste incinerator includes energy consumption, maintenance costs, and labor costs. When choosing a waste incinerator, its energy consumption and operating costs should be considered, and an economic analysis should be conducted. At the same time, it is also necessary to consider its demand for fuel and whether other auxiliary fuels need to be added.
Examine the degree of automation of the equipment With the development of technology, automation technology has been widely used in the control and monitoring of waste incinerators. When choosing a waste incinerator, its degree of automation should be considered, including automation control, monitoring systems, etc. Equipment with a high degree of automation can reduce labor costs, improve processing efficiency, and reduce the impact of human factors on the processing effect.
Consider the maintainability and after-sales service of the equipment The waste incinerator is a large-scale equipment that requires regular maintenance and maintenance. When choosing a waste incinerator, its maintainability should be considered, including factors such as the structure of the equipment and the replacement of wearing parts. At the same time, the quality and response time of after-sales service also need to be considered to ensure that the equipment is maintained and maintained in a timely manner during operation.
Incinerator Safety Precautions




Equipment maintenance and overhaul
Regular equipment maintenance and overhaul to ensure normal operation of the equipment and avoid safety problems caused by equipment failure.
Combustion control
The combustion of the incinerator must be sufficient to prevent the generation of harmful gases. At the same time, the combustion temperature must be controlled to prevent high temperature from causing damage to the furnace body.
Airtightness inspection
The furnace body and flue must be well sealed to prevent the leakage of harmful gases. Regular inspections and timely repair of leaks.
Reasonable slag discharge
The slag produced after incineration and the fly ash produced by flue gas treatment must be discharged reasonably to avoid secondary pollution to the environment.
Operator safety
Operators must strictly abide by the operating procedures to avoid safety problems caused by improper operation. At the same time, safety protection measures must be taken to ensure the health and safety of operators.
Monitoring system
Establish a complete monitoring system to monitor the combustion conditions, air flow, temperature and other parameters in the furnace in real time, and promptly detect and handle abnormal conditions.
Emergency handling
Be prepared for possible abnormal situations, and conduct emergency drills regularly to improve the emergency handling capabilities of operators.
Training and education
Train and educate operators to improve their safety awareness and operating skills, and ensure that they can operate correctly and safely.
Equipment cleaning
Clean the equipment regularly to prevent dust and debris from affecting the normal operation of the equipment, and avoid secondary pollution during the cleaning process.
Illegal operation
Operators must operate strictly in accordance with regulations, and illegal operations are prohibited to avoid safety accidents.
Some basics and required steps when designing an incinerator for heat recovery or waste treatment. This is particularly important for designers and students in developing countries where advanced design tools and computer modeling are not readily available. Waste management has become a major concern worldwide and among various waste treatment methods such as recycling and composting, incineration is the method of treating the non-reusable and non-organic portion of waste. Incineration is a complex process due to the heterogeneous nature of waste. Without understanding the relevant combustion science and the characteristics of the waste, it is impossible to properly design an incinerator. The first and foremost aspects that need to be considered in the design are: the combustion mechanism and its selection, the grate combustion system, the furnace geometry, the secondary air injection, the 3T, the heating value or calorific value of the waste, the theoretical air-fuel ratio and the excess air requirement. The incinerator internal size requirements, the combustion chamber size, the incinerator residence time and retention time, the air injection and the estimation of the fuel requirement and flame temperature need to be evaluated. No single method can be used to effectively treat all waste streams, so there is a need for an integrated waste management system that not only addresses the different methods of treating waste but also addresses issues such as waste streams, collection, environmental benefits, economic optimization and social acceptability.
Common Incinerator Types
Mass Burn Incinerators
The predominant type is used for untreated mixed municipal solid waste. High volume throughput continuous units thermally size and mix waste on grates or tumbling kilns.
Modular & Batch Incinerators
Used for consistent but smaller waste streams like industrial hazardous waste or sewage sludge. Pre-calculated batches result in optimized burns.
Rotary Kiln Incinerators
A rotating cylindrical kiln that agitates and conveys waste through the combustion chamber to control residence times. Used for hazardous waste, medical waste, and sludge.
Fluidized Bed Incinerators
Injects air from below into a bed of sand and waste materials, allowing mixing and transfer of oxygen across all waste for an efficient, complete burn.
Gasification & Pyrolysis Systems
Decompose waste via external heat to produce syngas for energy use while concentrating & reducing solids and contamination. Limited waste applications due to technical complexity.
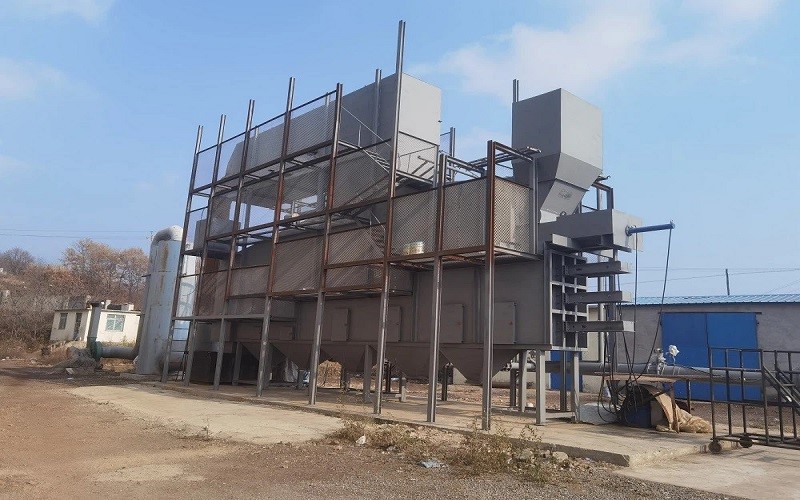
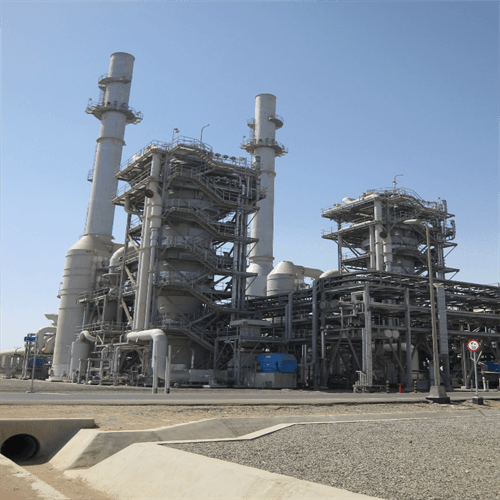
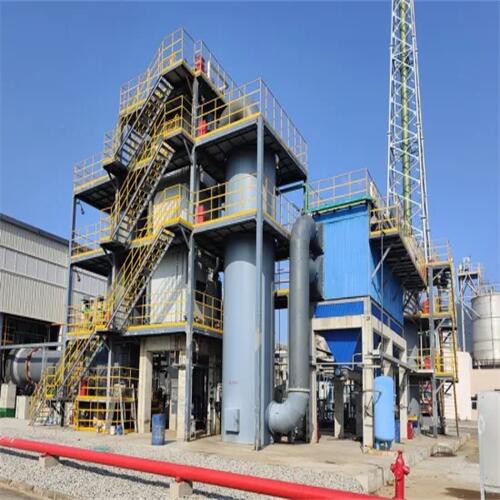
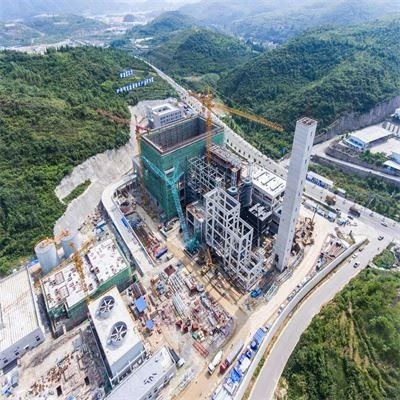
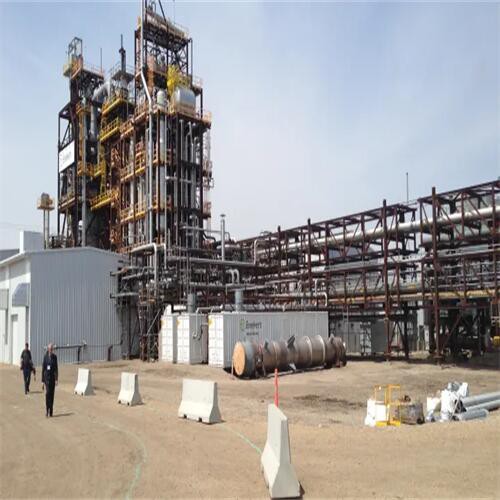
Our Factory
Tenor Low Carbon new Energy Technology (Liaoning) Co., Ltd. was established in 2021 and registered at the Industrial Incubation Base of Dalian University of Technology. Through cooperation with thermal power departments, environmental departments, mechanical departments, inorganic materials and other disciplines of HIT and Dalian University of Technology, the company focuses on designing and developing complete sets of small urban waste incineration technologies; Focusing on the application of technologies such as furnace arches, modular assembly, and dust reduction and dioxin removal inside the furnace to ensure full combustion of waste.