What is MSW incineration?
We have advanced production and processing technology, a professional design team, a complete quality assurance system, have obtained environmental standards and national licensing certifications, and have the ability to handle problems efficiently and timely.
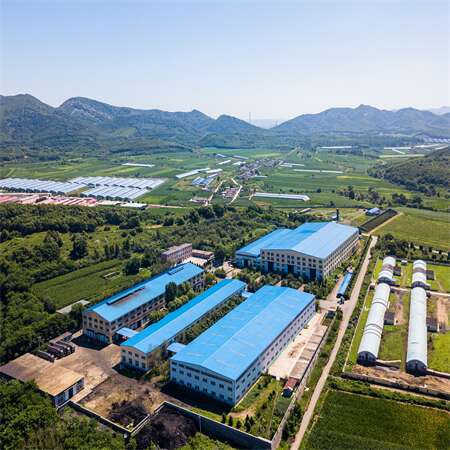

why choose Us ?
Tenor Low Carbon new Energy Technology (Liaoning) Co., Ltd. was established in 2021 and registered at the Industrial Incubation Base of Dalian University of Technology. Through cooperation with thermal power departments, environmental departments, mechanical departments, inorganic materials and other disciplines of HIT and Dalian University of Technology, the company focuses on designing and developing complete sets of small urban waste incineration technologies; Focusing on the application of technologies such as furnace arches, modular assembly, and dust reduction and dioxin removal inside the furnace to ensure full combustion of waste.
Products Description
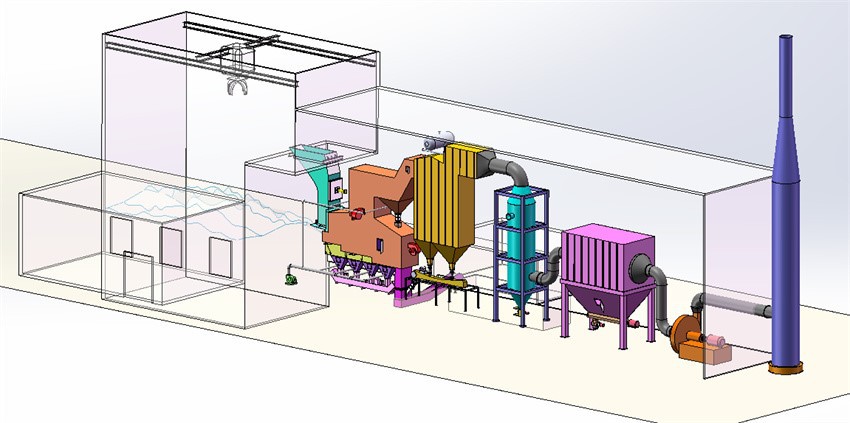
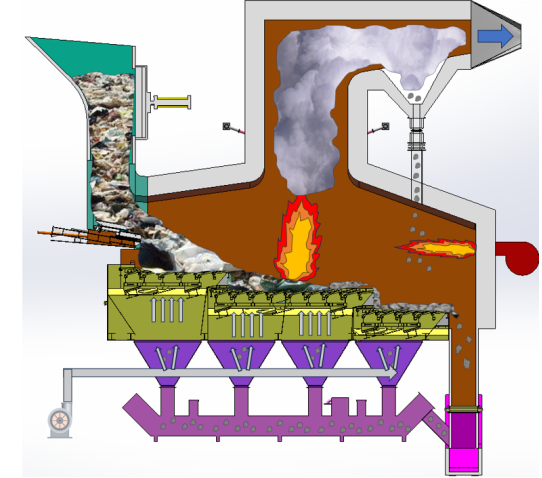
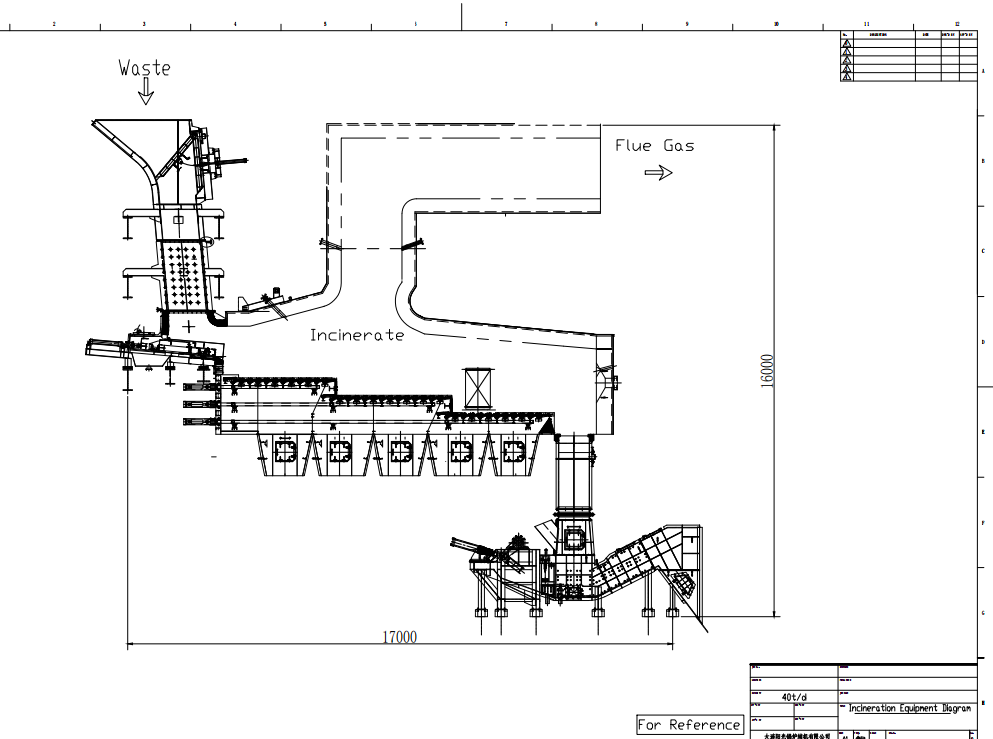
Tenor Low Carbon New Energy Technology Co., Ltd. developed a small waste incineration unit with the research team at Dalian University of Technology. WTE incineration systems include hoppers, feeding machines, stoker heaters, step grates, ash hoppers, slag removal systems, transport aircraft, combustion chambers, and transport aircraft.
Products Parameters
|
Scale (t/d) |
Number of furnaces |
Overall height of equipment (m) |
Floor space (m2) |
Emission standard |
|
50 |
1 |
17 |
60 |
《Pollution control standards for household waste incineration》 (GB18485-2014) |
|
100 |
1 |
17 |
75 |
|
|
150 |
2 |
17 |
90 |
|
|
200 |
2 |
17 |
105 |
|
|
250 |
3 |
17 |
12 |
Main equipment
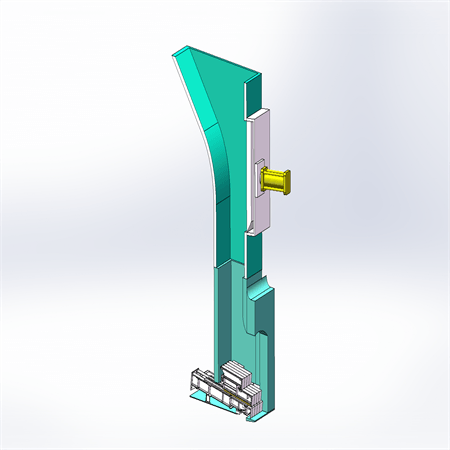
Feeding system
The feeding system is composed of hopper and feeder, and a gate is arranged inside the hopper. The gate not only ensures the sealing but also takes into account the function of breaking the "garbage bridge", and the "bridge" is broken through the gate movement when the garbage is blocked. The feeder and gate are driven by the hydro-cylinder, and the feeder can adjust the feeding speed according to the load of the incinerator.
Fire grate
Tenor made compact municipal waste incinerator adopts the step horizontal reciprocating grate (waste to energy system by moving grate incinerator), grate is divided into three stages of drying, burning and burning out zone, and the height drop between each grate is set, the garbage is scattered after falling, and the garbage is pushed to move while avoiding the incomplete combustion of garbage agglomeration. The reciprocating grate is driven by the hydro-cylinder, the three sections of the grate can be controlled independently, and the grate movement cycle can be adjusted according to the combustion state in the furnace. The grate is made of heat-resistant cast steel, which has good features of wear resistance, high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance.
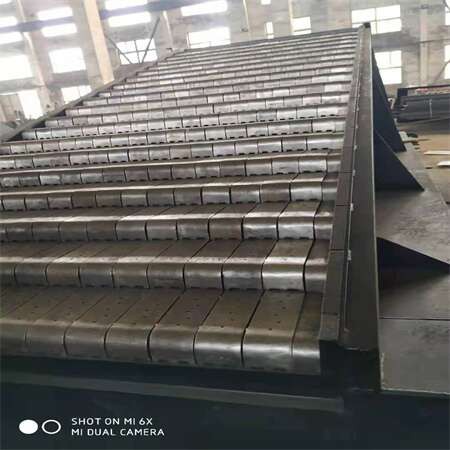
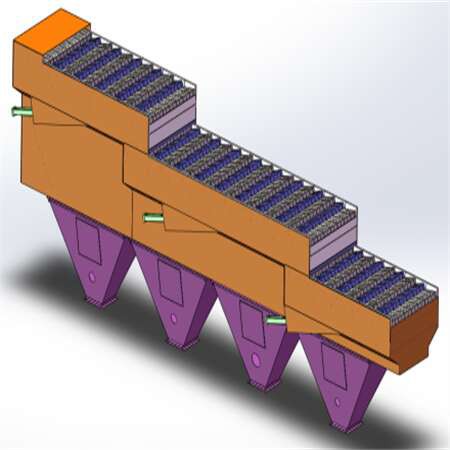

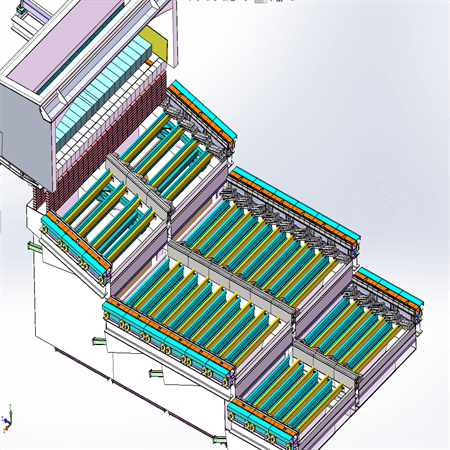
Grate advantages:
High efficiency stable combustion:
The garbage is fully burned, the thermal ignition reduction rate is low,Equipment performance: The grate has good wear resistance, high temperature resistance and corrosion resistance, low damage rate, low replacement frequency and low maintenance cost.The pores and gaps are matched with air inlet, and the overall air inlet effect is more uniform, which is conducive to uniform combustion and stable combustion.
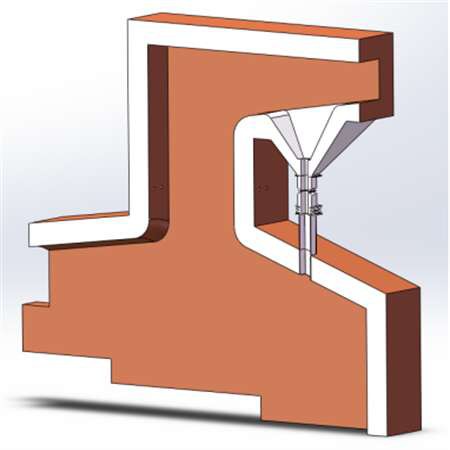
Incinerator
The combustion chamber above the grate is composed of front and rear arches and side walls. The furnace walls are built with thermal insulation cotton, castable material and refractory bricks. On the basis of the traditional incinerator structure, the front and rear arch structure is adjusted to enhance the heat radiation of the front and rear arch to the material layer, and the process of garbage drying and igniting is accelerated.
The secondary combustion chamber is arranged horizontally, compared with the traditional vertical flue, which reduces the overall height of the combustion system and reduces the construction cost. At the same time, the end of the secondary combustion chamber adopts a Spiral Separation structure and the principle of Tesla valve, which sends 90% of the fly ash in the flue gas back to the primary combustion chamber and enters the wet slag removal machine together with the ash. Effectively reduce the content of fly ash in the flue gas of the incinerator outlet and reduce the cost of follow-up treatment.
Solid waste incinerator process flow
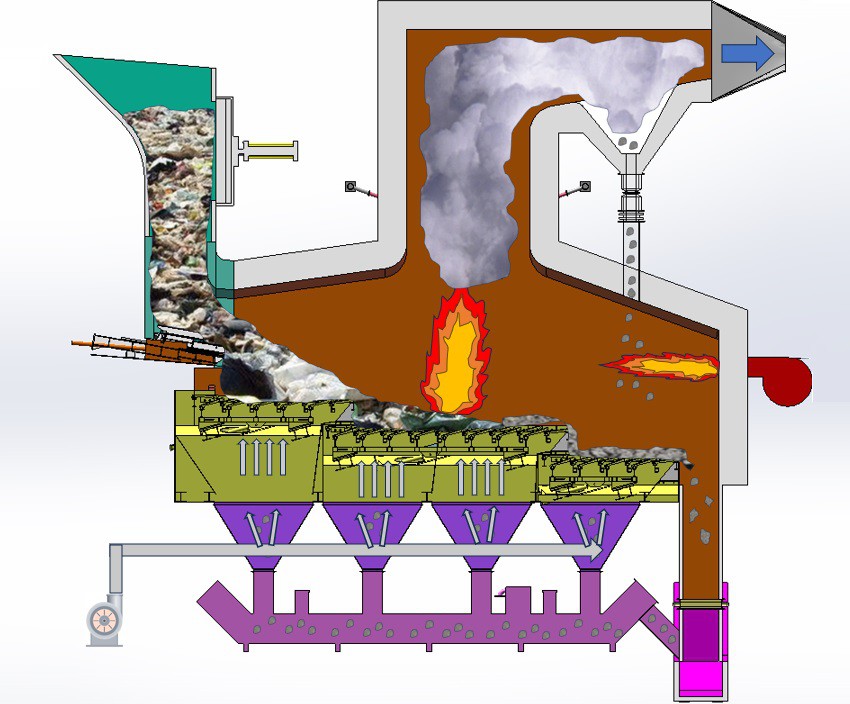
What is the process flow ?
After the garbage into the furnace through three sections of the grate: drying, burning, burning out, with a certain pressure and temperature. The garbage is pushed into the furnace in three parts: drying, burning and burning out, at a specific temperature and pressure.
The ash generated by complete combustion enters through the bucket of a wet slagging system and is then deposited in the slagpit. Under the air chamber is the horizontal ash leakage conveyer. A small amount of the ash and the slag below the grate are sent to the wet removal machine.
It is through the throat that the flue gases produced during combustion are introduced into the secondary combustion chamber. The secondary air added to the combustion chamber helps adjust furnace temperatures, control nitrogen oxide production, and ensure complete combustion.
The secondary combustion chamber temperature is between 850~1050. After the second combustion chamber, the flue gases stay in the chamber for at least 2 seconds. After heat transfer, the cooled flue gases are discharged through deacidification.
Process charateristics
- Easy installation, simple structure;
- Automate all equipment; reduce the workload of furnace personnel
- Construction costs are low and the total height of buildings is small.
- Secondary combustion chambers adopt a spiral dust-removal structure with a Tesla valve in order to reduce fly ash contents, lower the cost of dust removal, and increase the life expectancy.
- Heat burn is reduced by less than 5 %.
- Emissions of pollutants meet standard.
- Turn-key turn-key proposal with customized complete proposals and WTE equipment.
Waste to energy project display
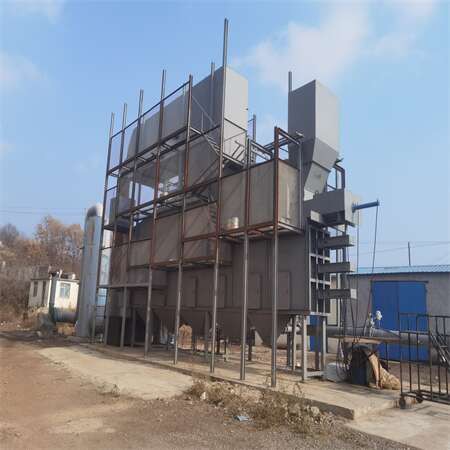
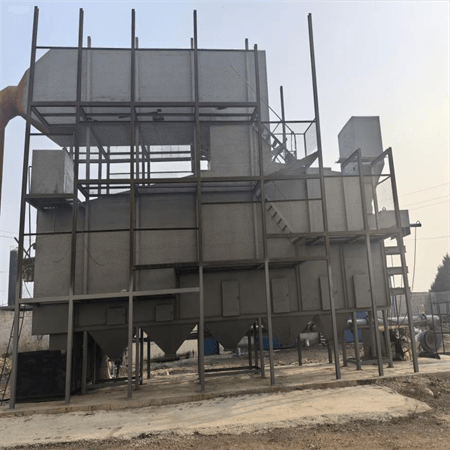


garbage incinerator 50 tons/d
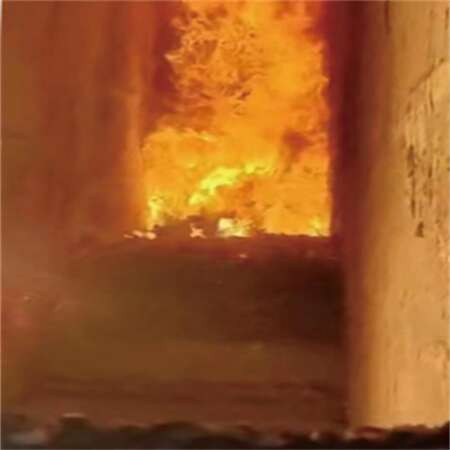
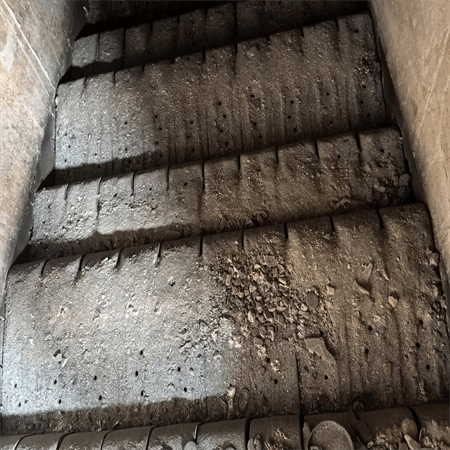


Benefite of Waste Management
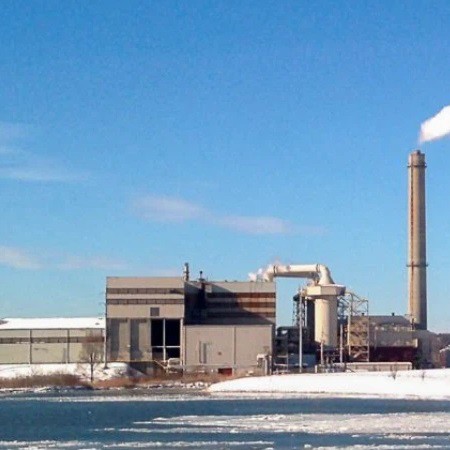
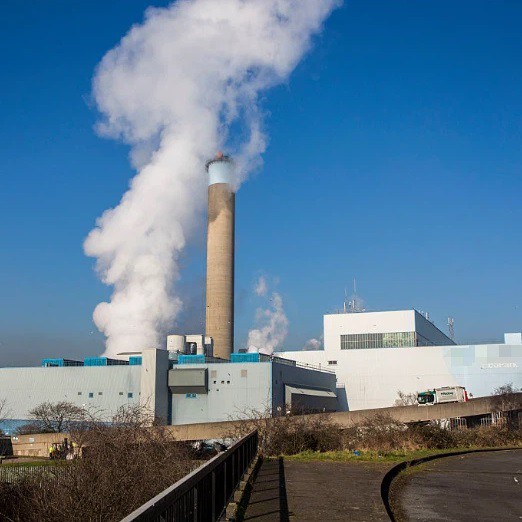
MSW incinerator can produce steam, hot water and electricity generation, sustainable Power from Small-Scale Waste Incineration.
where is application?
Township, cities and towns, government, power plant.




do you have any question?
What is incineration treatment of municipal solid waste?
Incineration is a waste-to-energy treatment process for reducing municipal solid waste (MSW) and hazardous waste. The process involves the combustion of waste materials at high temperatures in specially designed furnaces, called incinerators. During incineration, organic matter is oxidized and converted into carbon dioxide, water vapor, and other gases, while inorganic materials such as metals are reduced to their ash form.
The heat generated from the combustion process can be used to produce steam, which can then be used to generate electricity or provide heating for buildings. The ash produced during incineration can be processed and recycled into construction materials or safely disposed of in landfills.
Incineration is an effective method for reducing the volume of MSW by up to 90% and eliminating potentially hazardous materials. However, it also produces air pollutants such as particulates, dioxins, furans, and heavy metals, which require advanced emission control technologies to meet regulatory standards. Additionally, the process requires significant energy input and may not be economically viable for all types of waste.
What are the advantages of MSW incineration?
MSW incineration has several advantages, including:
1. Volume reduction: Incineration significantly reduces the volume of MSW, making it easier and more cost-effective to dispose of the remaining ash in landfills.
2. Energy recovery: The heat generated during incineration can be used to produce steam, which can then be used to generate electricity or provide heating for buildings. This helps to reduce reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions.
3. Efficient disposal: Incineration is a fast and efficient way to dispose of MSW, particularly in densely populated areas where landfill space is limited.
4. Disease control: Incineration kills bacteria and viruses present in MSW, reducing the risk of disease transmission.
5. Environmental benefits: Incineration reduces the amount of waste sent to landfills, which can help to prevent groundwater contamination and reduce greenhouse gas emissions from decomposing waste.
6. Versatility: Incineration can handle a wide range of waste materials, including hazardous and non-hazardous waste, making it a versatile waste management solution.
What are the three types of incineration?
There are three main types of incineration: mass burning, modular incineration, and rotary kiln incineration.
1. Mass burning: This is the most common type of incineration, where waste is burned in large furnaces at high temperatures (typically between 850-1650°C). The heat generated by the combustion process is used to produce steam, which can be used for electricity generation or heating purposes.
2. Modular incineration: This type of incineration is similar to mass burning but uses smaller, modular units that can be easily transported and assembled on-site. These units are typically used for smaller-scale waste disposal operations or temporary waste disposal needs, such as during disaster relief efforts.
3. Rotary kiln incineration: This type of incineration involves feeding waste into a rotating cylinder (kiln) that is heated from the outside. The waste is gradually moved through the kiln by the rotation and is exposed to high temperatures, which causes it to dry out, pyrolyze, and eventually burn. This method is often used for hazardous waste incineration because it can handle a wide range of waste types and can achieve very high destruction efficiencies.





