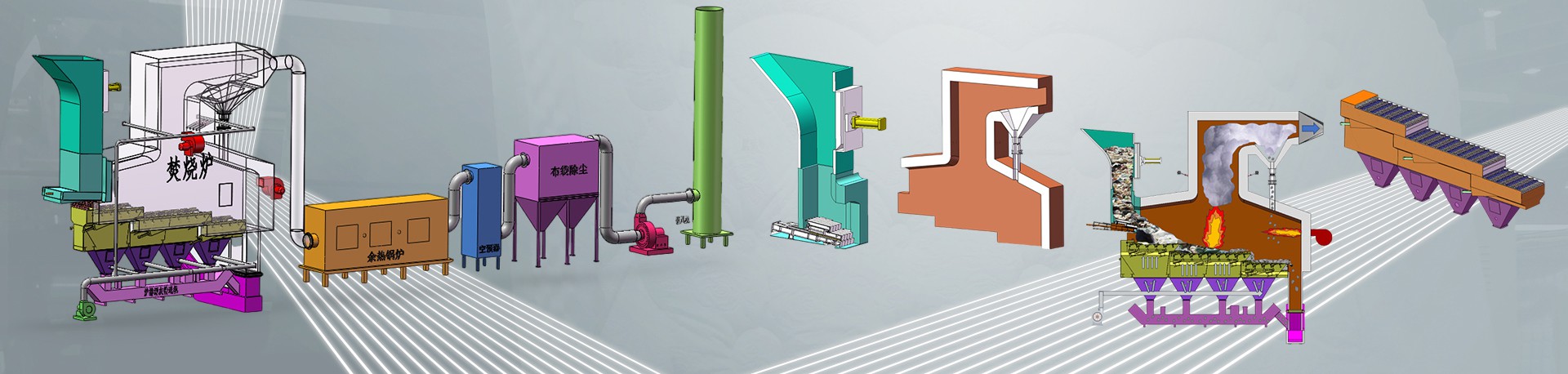
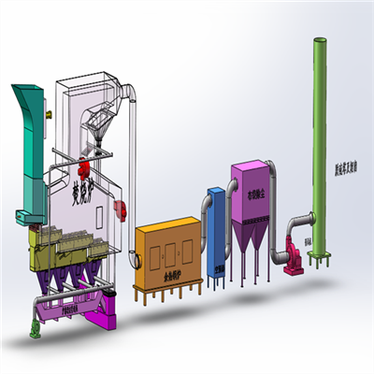
Garbage Furnace
An incinerator is a furnace for burning waste. Modern incinerators include pollution mitigation equipment such as flue gas cleaning.
Benefits of Garbage Furnace
Reduced Dependence on Transportation
Due to the low land requirement, waste incineration plants can be built near cities. This is helpful because it reduces the distance that waste has to be transported to the disposal site. This significantly reduces transportation costs and harmful gas emissions from cars during transportation, thereby reducing the overall carbon footprint. The transportation costs saved can be used for other purposes such as promoting community health and promoting the expansion of cities or regions.
Better Control of Odor and Noise
Instead of decomposing in the open air, a way to cause air pollution, waste is burned in facilities where the byproducts of the incineration process can be controlled, thereby reducing unpleasant odors. In addition, methane produced in landfills can cause explosions, thereby creating noise pollution, which is unheard of in incineration plants.
Prevents the Production of Methane Gas
When waste decomposes in landfills, it produces a lot of methane, which is the main cause of global warming. Methane is both harmful to the environment and flammable, making it a safety threat. Since they do not emit methane, they are safer and more environmentally friendly.
Eliminate Harmful Bacteria and Chemicals
Incineration plants use extremely high temperatures to eliminate harmful microorganisms and chemicals in waste. Therefore, it is a very successful strategy to reduce medical waste.
Operates in any weather
Since waste incinerators are enclosed structures, they can operate regardless of the weather. Garbage cannot be placed in landfills during the rainy season because rainwater may wash dangerous chemicals into the ground and form leachate, contaminating groundwater and surrounding land. Garbage cannot be dumped when it is windy because it will be blown into the environment. In contrast, incinerators are less susceptible to weather fluctuations because they do not leak when burning garbage. Incinerators operate 24 hours a day and waste management is more efficient than at landfills.
It has a computerized monitoring system
Governments, towns, institutions, and commercial waste management companies can purchase incinerators equipped with computer equipment to diagnose most problems. This will enable operators to detect problems before they worsen and become too expensive. Computers will also facilitate the operators' jobs because they will be able to monitor the efficiency of the incinerator's operation.
Why Choose Us
Advanced equipment
We take strong measures to ensure that we use the highest quality equipment in the industry and that our equipment is regularly and meticulously maintained.
Rich experience
Has a long-standing reputation in the industry, which makes it stand out from its competitors. With over many years of experience, they have developed the skills necessary to meet their clients' needs.
Efficient and convenient
The company has established marketing networks around the world to provide high-quality services to customers in an efficient and convenient manner.
Quality assurance
In terms of quality assurance, the company strictly follows the standards and norms of the industry quality system. Adopt industry-leading testing equipment to ensure product quality and good reputation.
Professional team
We have a team of skilled and experienced professionals who are well-versed in the latest technology and industry standards. Our team is dedicated to ensuring that our customers get the best service and support possible.
Competitive prices
We offer our products at competitive prices, making them affordable for our customers. We believe that high-quality products should not come at a premium, and we strive to make our products accessible to all.
What Are the Technological Innovations of Garbage
High-efficiency combustion technology
High-efficiency combustion technology is one of the important directions of technological innovation of garbage incinerators. By improving the design of the combustion chamber, optimizing the air supply and fuel mixing, and adopting advanced combustion control systems, the combustion efficiency of garbage incinerators has been significantly improved. This not only reduces energy waste, but also improves the stability and reliability of garbage incineration.
Low nitrogen oxide combustion technology
In response to the problem of nitrogen oxide emissions generated during garbage incineration, researchers have developed low nitrogen oxide combustion technology. Through selective catalytic reduction (SCR) technology or selective non-catalytic reduction (SNCR) technology and other means, the generation and emission of nitrogen oxides are effectively reduced, reducing pollution to the atmosphere.
Flue gas treatment technology
The innovation of flue gas treatment technology is also an important manifestation of the technological progress of garbage incinerators. The use of activated carbon adsorption, wet dust collector, bag dust collector and other technologies to purify the flue gas can effectively remove harmful substances in the flue gas, such as sulfur dioxide, particulate matter, etc., to ensure that the flue gas emissions meet environmental protection standards.
Ash resource utilization technology
As the concept of resource utilization has become more popular, ash resource utilization technology has also received widespread attention. By converting the ash produced by garbage incineration into valuable resources, such as building materials, landfill cover materials, roadbed materials, etc., it not only reduces the potential harm of ash to the environment, but also realizes the recycling of resources.
Intelligent technology
The application of intelligent technology has brought revolutionary changes to the operation and management of garbage incinerators. By introducing advanced technologies such as the Internet of Things, big data, and artificial intelligence, garbage incinerators have achieved intelligent control and optimized management. The intelligent control system can monitor the composition, water content, calorific value and other parameters of garbage in real time, automatically adjust the combustion conditions, and ensure the stability and economy of garbage incineration. At the same time, intelligent fault diagnosis technology can provide early warning and diagnosis of equipment failures, reducing the maintenance cost and downtime of equipment.
New incineration technology
In recent years, new incineration technologies such as low-temperature magnetization degradation furnaces have also been gradually applied. This technology reduces the emission of harmful gases and pollutants by reducing the participation of oxygen. At the same time, its high efficiency, energy saving, and environmental protection make it a scientific and technological innovation in the field of garbage treatment.
Primary Chamber
This is where the waste is initially loaded and burned. The primary chamber allows the waste to vaporize, and the low air-to-fuel ratio helps in drying and carbon combustion.
Secondary Chamber
The waste-derived volatile substances from the primary chamber are transferred to the secondary chamber. Here, additional air is injected to ensure complete combustion of the volatile gases. The higher temperatures in the secondary chamber promote the oxidation of gaseous products.
Flue Stack
Also known as the chimney, the flue stack is responsible for releasing the exhaust gases into the atmosphere. The stack height requirements vary depending on local regulations and environmental considerations.
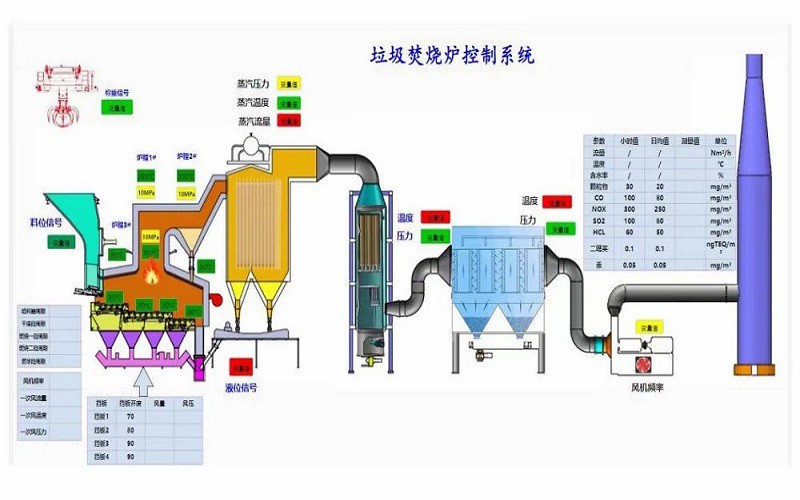
Control Panel and Thermocouples
These components regulate and monitor the incinerator’s operation. They ensure that the chambers reach the required temperature before loading waste for incineration.
Burners
Burners are used to heat up the incinerator, and they are often turned off during the combustion process. Modern incinerators may include low NOx or variable gas flow burners.
Fuel Tanks
Fuel tanks store the fuel, which can be solid waste, used by the burners during the incineration process.
Combustion Chamber (Primary Chamber)
The primary chamber is where the waste is loaded and ignited. It operates at high temperatures, reducing the waste to ash and gases.
Pollution Control Equipment
This includes filters, scrubbers, and other devices that remove pollutants from the exhaust gases before they are released into the atmosphere. These control measures ensure compliance with environmental regulations.
Ash Handling
Ash handling equipment is responsible for collecting and disposing of the ash produced during the incineration process.
Electrical Equipment
Generators, control systems, and other electrical components are used to operate and control the incinerator.
Cooling System
The cooling system helps reduce the temperature of the exhaust gases before they are released into the atmosphere. This ensures that the gases are safe to be discharged.
Stack
The stack, also known as the chimney or flue stack, is the component that exhausts the gases into the atmosphere.
Applications of Incinerator
Medical waste
Medical wastes generated from laboratories, hospitals, and health clinics can pose health risks if not properly treated or disposed of. Incinerators are designed to destroy and neutralize medical waste.
Animal waste
Incinerators are employed to dispose of animal wastes, including carcasses, waste, and byproducts, thereby preventing the spread of infection and viruses.
General waste
General wastes include less harmful wastes from sites such as mining, small communities, and military operations, which must be destroyed to reduce environmental impact. Thus, incinerators are devised to incinerate such wastes.
Nanomaterial wastes
Incinerators are utilized to dispose of nanomaterial wastes such as consumer products in municipal solid waste, wastes from nanotechnology research and development, hazardous wastes, etc.
How Is the Energy Distribution of Domestic Waste Incinerators Completed
Transportation and storage of garbage
Domestic waste is first collected and transported to the waste incineration plant. Before entering the incinerator, the garbage needs to be stored and pre-treated. The storage link is mainly to balance the output of garbage and the processing capacity of the incinerator so that the garbage can enter the incinerator evenly. At the same time, the pretreatment link includes crushing, screening and sorting the garbage to remove large garbage, paper, plastic, glass and metal and other recyclables, reduce the amount of garbage entering the incinerator, and increase the calorific value of the garbage.
Combustion process
Domestic waste is burned in the incinerator to release heat. During the combustion process, the organic matter in the garbage reacts chemically with oxygen to generate carbon dioxide and water vapor, while releasing a large amount of heat. Part of this heat is used to maintain the temperature in the waste incinerator, and the other part is converted into steam or electricity through the waste heat recovery system.
Waste heat recovery
Waste heat recovery is an important part of the energy distribution of domestic waste incinerators. The heat generated during the combustion process is converted into steam or electricity through the waste heat recovery system. The recovered energy can be used for heating, power generation and other purposes to achieve energy recycling. Common waste heat recovery methods include waste heat boilers and gas turbine combined cycle power generation. Waste heat boilers can convert the heat in the high-temperature flue gas generated by combustion into steam for heating or driving steam turbines to generate electricity. The gas turbine combined cycle power generation directly sends the high-temperature flue gas into the gas turbine, mixes it with air and burns it to generate mechanical energy, and then converts it into electrical energy through the generator.
Flue gas treatment
During the combustion and waste heat recovery process, a large amount of flue gas will be generated. These flue gases contain a variety of harmful substances, such as sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, heavy metals, etc., which need to be purified before they can be discharged. The flue gas treatment system includes desulfurization, denitrification and dust removal, which can effectively remove harmful substances in the flue gas and reduce pollution to the environment. The treated flue gas is finally discharged into the atmosphere through the chimney.
Residue treatment
Some residues, including slag and fly ash, will be generated during the incineration of domestic waste. These residues need to be properly handled to avoid impacts on the environment and human health. Slag can be recycled after cooling, crushing and screening, such as making building materials. Fly ash needs to be solidified to stabilize the harmful substances in it, and then safely landfilled or recycled.
Incinerators are engineered to safely combust waste while recovering energy and dramatically reducing volumes sent to landfills.
Strict emissions control technology ensures minimally regulated air releases under standard operations that are protective of human health.
Incineration is a part of balanced solid waste management plans also emphasizing reductions, reuse, recycling, composting, and material recovery.
Modern incinerators are vastly advanced compared to historic incinerators and bear zero resemblance to outdated burners that lack extensive process and emissions controls.
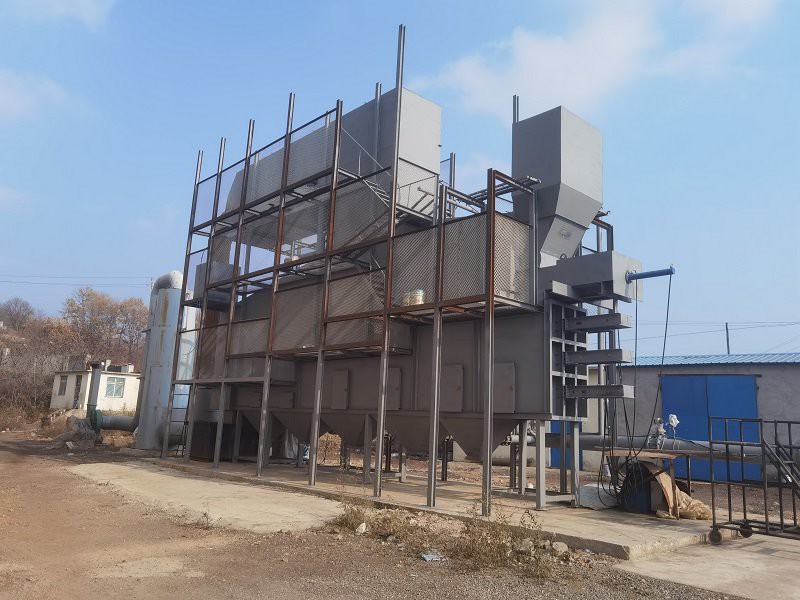

What Are the Precautions for the Maintenance of Garbage Incinerators
Regular cleaning
Regularly clean the residue and ash inside the incinerator to keep the furnace clean to ensure normal combustion effect.
Inspection and replacement
Regularly check the various components of the incinerator, such as transmission components, control system, etc., to ensure that they can operate normally.
Check the smoke exhaust system
Ensure that the smoke exhaust system is unobstructed to avoid smoke backflow or retention in the furnace due to poor smoke exhaust, which affects the combustion effect.
Check protective facilities
Regularly check and maintain protective facilities, such as temperature monitoring, pressure monitoring, alarm system, etc., to ensure that they can work normally in an emergency.
Fuel management
Use appropriate fuel and avoid using materials that do not meet the requirements to avoid damage to equipment or accidents such as fire and explosion. Regularly check the storage and use of fuel to ensure timely supply and reasonable use of fuel.
Lubrication and maintenance
Regularly lubricate and maintain bearings, gears and other components in the incinerator to reduce wear and friction and extend the service life of the equipment.
Record maintenance history
Record the history of each maintenance, including the maintenance date, maintenance content and replaced parts. This helps to track the maintenance of the equipment and detect potential problems in a timely manner.
Notes on long-term out-of-service
If the incinerator needs to be out of service for a long time, the main oil circuit and power supply switches should be turned off.
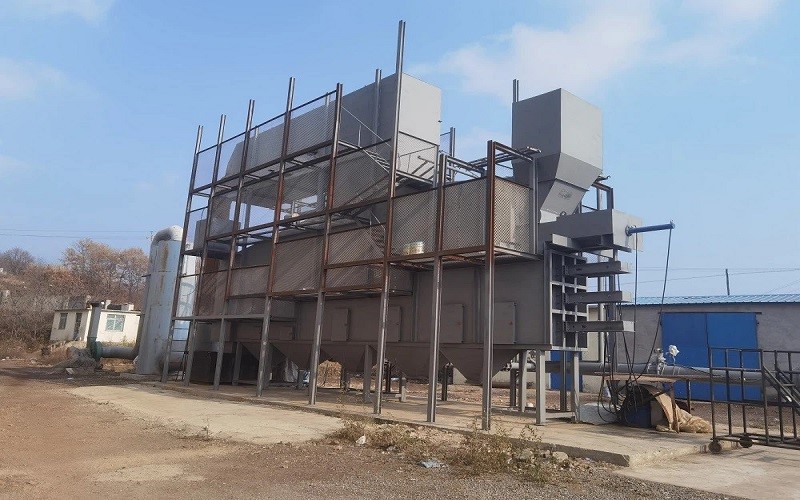
Our Factory
Tenor Low Carbon new Energy Technology (Liaoning) Co., Ltd. was established in 2021 and registered at the Industrial Incubation Base of Dalian University of Technology. Through cooperation with thermal power departments, environmental departments, mechanical departments, inorganic materials and other disciplines of HIT and Dalian University of Technology, the company focuses on designing and developing complete sets of small urban waste incineration technologies; Focusing on the application of technologies such as furnace arches, modular assembly, and dust reduction and dioxin removal inside the furnace to ensure full combustion of waste.





FAQ
As one of the most professional garbage furnace suppliers in China, we're featured by quality products and good service. Please rest assured to buy high-grade garbage furnace made in China here from our factory.
waste management incinerators, waste incineration production line, waste incinerator smokeless