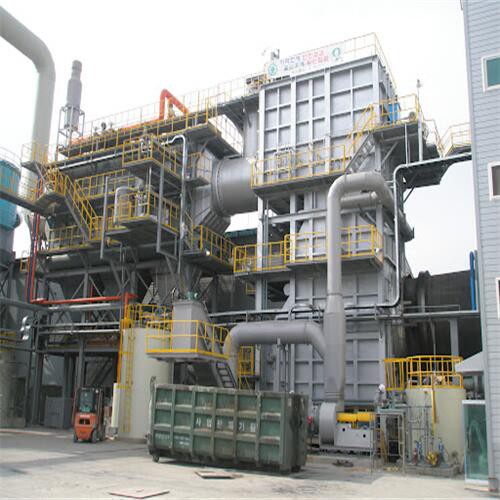
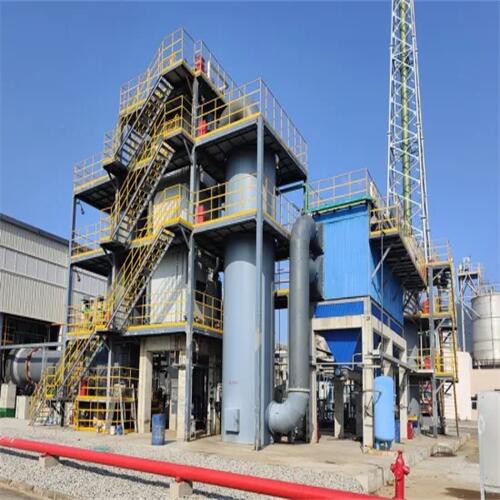
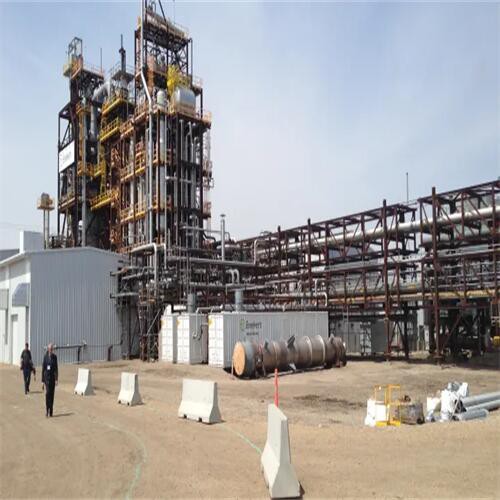
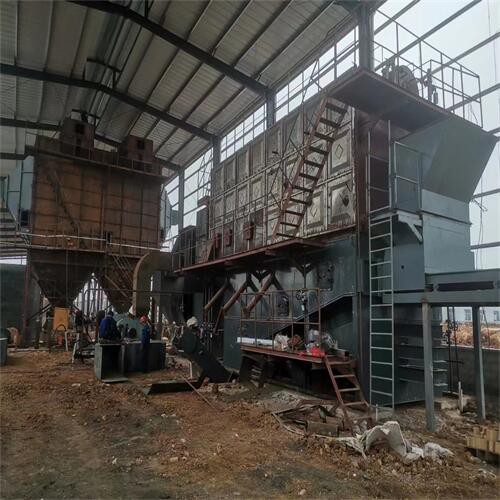
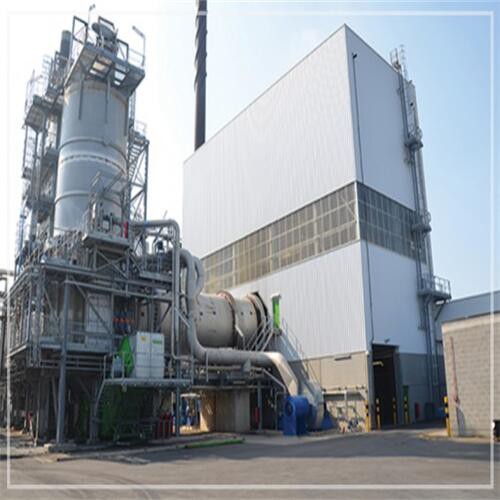
An incinerator machine is a mechanical unit that is built to destroy waste. this happens by burning the waste at an extremely high temperature, reducing it to bottom ash. The machines can be manufactured from small garden waste incinerators, all the way to large scale industrial sized machines.
Benefits of Incinerator Waste Processing Machine
Reduction
Waste incinerators can reduce the amount of waste, greatly reducing the volume and weight of waste and reducing the cost of waste treatment.
Harmless treatment
Waste incinerators can completely burn waste at high temperatures, effectively reducing the emission of harmful gases and achieving harmless treatment of waste.
Resource utilization
Waste incinerators can recycle the heat generated by incineration for power generation or heating, achieving resource recycling.
Environmental protection and energy saving
Waste incinerators use advanced flue gas purification systems, which can effectively remove harmful substances in flue gas and reduce pollutant emissions. At the same time, the energy recovery function also greatly improves energy utilization efficiency.
Economic benefits
Waste incinerators can achieve waste reduction, harmlessness and resource treatment, greatly reducing the cost of waste treatment and having good economic benefits.
Why Choose Us
Advanced equipment
We take strong measures to ensure that we use the highest quality equipment in the industry and that our equipment is regularly and meticulously maintained.
Rich experience
Has a long-standing reputation in the industry, which makes it stand out from its competitors. With over many years of experience, they have developed the skills necessary to meet their clients' needs.
Efficient and convenient
The company has established marketing networks around the world to provide high-quality services to customers in an efficient and convenient manner.
Quality assurance
In terms of quality assurance, the company strictly follows the standards and norms of the industry quality system. Adopt industry-leading testing equipment to ensure product quality and good reputation.
Professional team
We have a team of skilled and experienced professionals who are well-versed in the latest technology and industry standards. Our team is dedicated to ensuring that our customers get the best service and support possible.
Competitive prices
We offer our products at competitive prices, making them affordable for our customers. We believe that high-quality products should not come at a premium, and we strive to make our products accessible to all.
As the amount of waste generated by human activities continues to increase, it is becoming increasingly important to find effective and environmentally friendly solutions to deal with this waste. One widely adopted technology is the use of waste-to-energy plants, also known as waste-to-energy incinerators or waste-to-energy facilities.
Municipal Solid Waste Incinerator
Municipal solid waste incinerator is an effective way to handle the increasing amount of trash in urban areas. This type of incinerator is designed to burn solid waste, including household garbage, industrial waste, and medical waste. The goal is to reduce the volume of the waste by up to 90% and convert it into ash and gas emissions.
Tenor made small waste incineration system was developed by Tenor Low Carbon New Energy Technology (Liaoning) Co., Ltd. and Dalian University of Technology research team. WTE incineration system including hopper, feeding machine, stoker furnace, step grate, ash hopper, slag removal system, transport aircraft and combustion chamber, suitable for daily capacity of 50 to 250 tons/d of small domestic waste incineration projects.
Tenor made small waste incineration system was developed by Tenor Low Carbon New Energy Technology (Liaoning) Co., Ltd. and Dalian University of Technology research team. WTE incineration system including hopper, feeding machine, stoker furnace, step grate, ash hopper, slag removal system, transport aircraft and combustion chamber, suitable for daily capacity of 50 to 250 tons/d of small domestic waste incineration projects.
Tenor made small waste incineration system was developed by Tenor Low Carbon New Energy Technology (Liaoning) Co., Ltd. and Dalian University of Technology research team. WTE incineration system including hopper, feeding machine, stoker furnace,step grate, ash hopper, slag removal system, transport aircraft and combustion chamber, suitable for daily capacity of 50 to 250 tons/d of small domestic waste incineration projects.
We provide high -quality products, professional services, customized solutions.
Municipal Solid Waste Incineration Plant
Our municipal solid waste incineration plant is a state-of-the-art facility designed to effectively and efficiently dispose of urban waste. With advanced technology and strict environmental standards, our plant can safely and sustainably handle large volumes of solid waste, while minimizing emissions and reducing landfill waste.
Our waste to energy incinerator is an advanced and eco-friendly solution for managing waste. With this incinerator, waste is converted to energy, reducing the amount of waste disposed in landfills and producing electricity or heat for various applications. Our incinerator features advanced technologies that ensure efficient and clean combustion, resulting in lower emissions and better air quality.
The Impact of Incinerators on Human Health and Environment
Of the total wastes generated by health-care organizations, 10%-25% are biomedical wastes, which are hazardous to humans and the environment and requires specific treatment and management. For decades, incineration was the method of choice for the treatment of such infectious wastes. Incinerator releases a wide variety of pollutants depending on the composition of the waste, which leads to health deterioration and environmental degradation. The significant pollutants emitted are particulate matter, metals, acid gases, oxides of nitrogen, and sulfur, aside from the release of innumerable substances of unknown toxicity. This process of waste incineration poses a significant threat to public health and the environment. The major impact on health is the higher incidence of cancer and respiratory symptoms; other p otential effects are congenital abnormalities, hormonal defects, and increase in sex ratio. The effect on the environmental is in the form of global warming, acidification, photochemical ozoneor smog formation, eutrophication, and human and animal toxicity. Thus, there is a need to skip to newer, widely accepted, economical, and environment-friendly technologies. The use of hydroclaves and plasma pyrolysis for the incineration of biomedical wastes leads to lesser environmental degradation, negligible health impacts, safe handling of treated wastes, lesser running and maintenance costs, more effective reduction of microorganisms, and safer disposal.
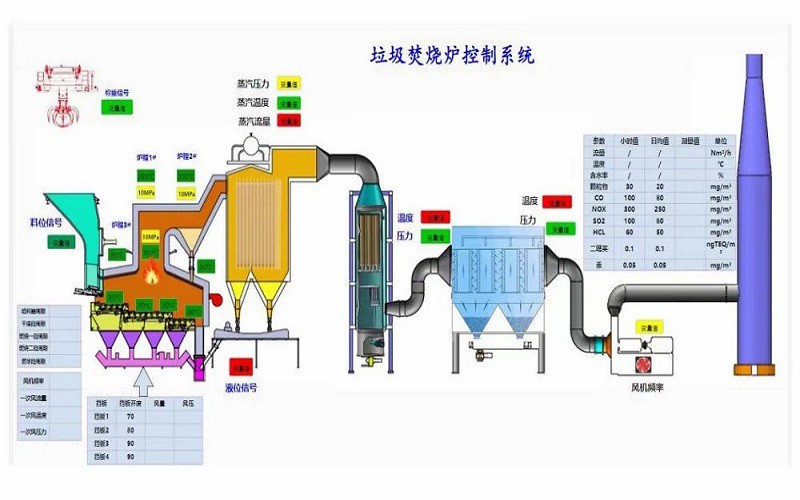
The Waste Incineration Process
Waste preparation
Oversized items are removed and certain recyclables like metals are recovered. The remaining waste is often shredded before it enters the incinerator.
Combustion
Waste is burned in an oxygenated single combustion chamber. Materials are burned at extremely high temperatures of 1,800-2,200 degrees Fahrenheit. At those temperatures, waste should be completely combusted, leaving nothing but gases and ash.
Energy recovery
The gases released during combustion are cooled with water, generating steam through heat recovery. The steam is used to power electrical generators.
Environmental control
The cooled gas is treated by scrubbers, precipitators, and filters to remove pollutants. The solids that form during treatment, called residuals, are disposed of in a landfill.
Environmental release
The treated gas is released into the atmosphere. There should be no visible smoke from the smokestack because the remaining gases should be free from particulates.
Types of Incinerator
Rotary Kiln Incinerator
The basic design consists of two thermal treatment chambers: a primary chamber that is slightly slanted and into which waste is fed (along with hot exhaust air containing oxygen), rotated, and thermally decomposed by heat radiation from the secondary chamber; and a recombustion chamber that is located at the back of the kiln and into which the decomposition air and the remaining waste is completely burned with the supply of secondary air. It is built with a rotating combustion chamber that keeps the garbage circulating continually. The waste can vaporize, which makes burning easier. By modifying the inclination angle and rotational rate of the kiln, the waste throughput rate can be managed. Solids burnout rates and particulate entrapment in the flue gas are higher for rotary kiln incinerators than for other incinerator designs due to the waste' s turbulent motion in the primary chambers. Because of this, gas cleaning accessories are frequently added to rotary kiln incinerators.
Waste-Gas Flare Incinerator
In many industrial activities, including oil-gas extraction, refineries, chemical plants, the coal industry, and landfills, undesirable or excess gases and liquids are discharged. Gas flaring is a combustion device used to burn these gases and liquids. A substantial source of greenhouse gas emissions is gas flaring. Additionally, it produces heat and noise and renders a lot of space uninhabitable. It is used for non-hazardous waste with high organic content.
Moving Grate Incinerator
The waste is burned in layers on the grate that moves the waste through the furnace in a traditional mass-burning incinerator based on a moving grate. On the grate, the waste is dried before being burned at a high temperature with an air supply.
The non-combustible waste fractions, which include the ash, exit the grate through the ash chute as slag (bottom ash). The bottom ash (slag), which drops into the water trap of the slag pusher from the grate' s end, is then cooled by coming into contact with cooling water before moving on to the conveyor system. Typically, 10 to 25 percent of the weight of the waste feed is made up of slag.
The main benefits of the moving grate are its well-proven technology, ability to accept wide variations in waste composition and heat values, and ability to be produced in extremely large units. The primary drawback is the expense, which is relatively significant for investment and maintenance.
Multiple Hearth Incinerator
A multiple hearth incinerator consists of a row of circular hearths arranged in a column and protected by a steel shell lined with refractory with operating temperatures ranging from 1400 to 1800°F. The feed material is moved across each hearth in a spiral pattern by rabble arms attached to a vertical rotating shaft that runs through the furnace' s center before dropping through the openings into the hearth below. The finished product is ejected through an outlet after traversing through each hearth.
Liquid Injection Incinerator
A frequently used device that uses high pressure to split liquid wastes into tiny droplets for rapid burning. Wastes are delivered through nozzles and atomized into small droplets to enable the greatest possible mixing with air with operating temperatures ranging from 1200 to 3000°F. The feed must behave as a liquid with a viscosity of no more than 10,000 ssu. A solid can be used if it can be melted and pumped and can completely combust organic combustible material and non-combustibles like impurities in water.
Fixed Grate/ Direct-Flame Incinerator
It is often the most widely produced and utilized. Fuel and oxygen are used to maintain the direct flame, allowing trash to be burned. When waste gas contains particles, direct flame incinerators are employed. They run between 1000 and 1500 °F.
Applications of Incinerator
Medical waste
Medical wastes generated from laboratories, hospitals, and health clinics can pose health risks if not properly treated or disposed of. Incinerators are designed to destroy and neutralize medical waste.
Animal waste
Incinerators are employed to dispose of animal wastes, including carcasses, waste, and byproducts, thereby preventing the spread of infection and viruses.
General waste
General wastes include less harmful wastes from sites such as mining, small communities, and military operations, which must be destroyed to reduce environmental impact. Thus, incinerators are devised to incinerate such wastes.
Nanomaterial wastes
Incinerators are utilized to dispose of nanomaterial wastes such as consumer products in municipal solid waste, wastes from nanotechnology research and development, hazardous wastes, etc.
Parts of Incinerator
Primary chamber
All garbage will be fed into the primary chamber and burned for the first time there. The primary chamber is where the waste vapourises. The low air-to-fuel ratio in this starved-air chamber causes the waste to dry out and makes it easier for it to evaporate, burning up most of the carbon.
Secondary chamber
Waste-derived volatile/gasified substances are transferred to the secondary chamber. To complete combustion, more air is injected in the second stage into the volatile gases created in the initial chamber. Temperatures in the secondary chamber are higher than those in the primary chamber. Due to the appropriate residence time, high temperature, and 100% surplus air in the secondary chamber, the gaseous products (volatile material) are oxidized. The gases are handled after they exit the secondary chamber.
The gases are introduced to the droplet separator, where the moisture is taken out of the gases. This lowers the temperature of the flue gas, making it safe to release into the atmosphere.
Flue Stack
The term "chimney" also applies to chimneys. Most incinerators have a chimney height requirement of 3 meters or more. This requirement would be higher in places with a larger population or where the atmosphere requires it.
Control panel and thermocouples
These regulate the machine' s operation and guarantee that the chambers are heated up before any waste is loaded for incineration. Depending on the type of waste, the settings can be tailored to the operator' s needs.
Burners
These are utilized to warm the incinerator up and are often turned off throughout the burning process.
Fuel tanks
The fuel is kept in storage. During the operation of the incinerator, the burners will have direct lines into the tank.
Regular Servicing
We offer regular servicing of incinerators, typically conducted every 6 or 12 months. This service involves a thorough inspection to identify and rectify any potential issues before they escalate. Our preventative maintenance approach ensures the smooth operation of your incinerator and helps to prolong its lifespan. We also replace components that have reached the end of their useful life, ensuring your incinerator remains in peak condition.
Repairs
Our team is skilled in a wide range of repair services, including burners, fans, feeder, and refractory repairs. We understand the critical role these components play in the overall operation of your incinerator, and we are committed to restoring them to their optimal functionality.
Incinerator Optimization
We offer incinerator optimization services, focusing on burner and combustion processes. Our goal is to enhance the efficiency of your incinerator, which in turn reduces your operational expenditure and environmental footprint.
Incinerator Emission Compliance
Meeting regulatory and emission compliance standards is a crucial aspect of incinerator operation. We are here to ensure your incinerator is ready to meet these standards.
Our team provides the necessary maintenance services to keep your incinerator running smoothly and efficiently. We focus on optimizing combustion processes to ensure minimal emissions, helping you meet and maintain compliance with emission regulations.
Meeting emission compliance standards may require upgrades to your incinerator system. Our team of skilled engineers is ready to provide these upgrades, ensuring your incinerator is up-to-date with the latest emission reduction technologies. We handle everything from the initial assessment to the final implementation, ensuring your incinerator is fully compliant and operates at peak efficiency.
Operator Training
Recognizing the frequent changes in operators, we provide comprehensive training to ensure the safety and efficiency of incinerator operation. Our training covers the correct procedures for daily and weekly maintenance checks and operation, in compliance with Health and Safety regulations. We believe that a well-trained operator is key to maintaining the efficiency and longevity of your incinerator.
Our Factory
Tenor Low Carbon new Energy Technology (Liaoning) Co., Ltd. was established in 2021 and registered at the Industrial Incubation Base of Dalian University of Technology. Through cooperation with thermal power departments, environmental departments, mechanical departments, inorganic materials and other disciplines of HIT and Dalian University of Technology, the company focuses on designing and developing complete sets of small urban waste incineration technologies; Focusing on the application of technologies such as furnace arches, modular assembly, and dust reduction and dioxin removal inside the furnace to ensure full combustion of waste.