why choose us
why choose our products
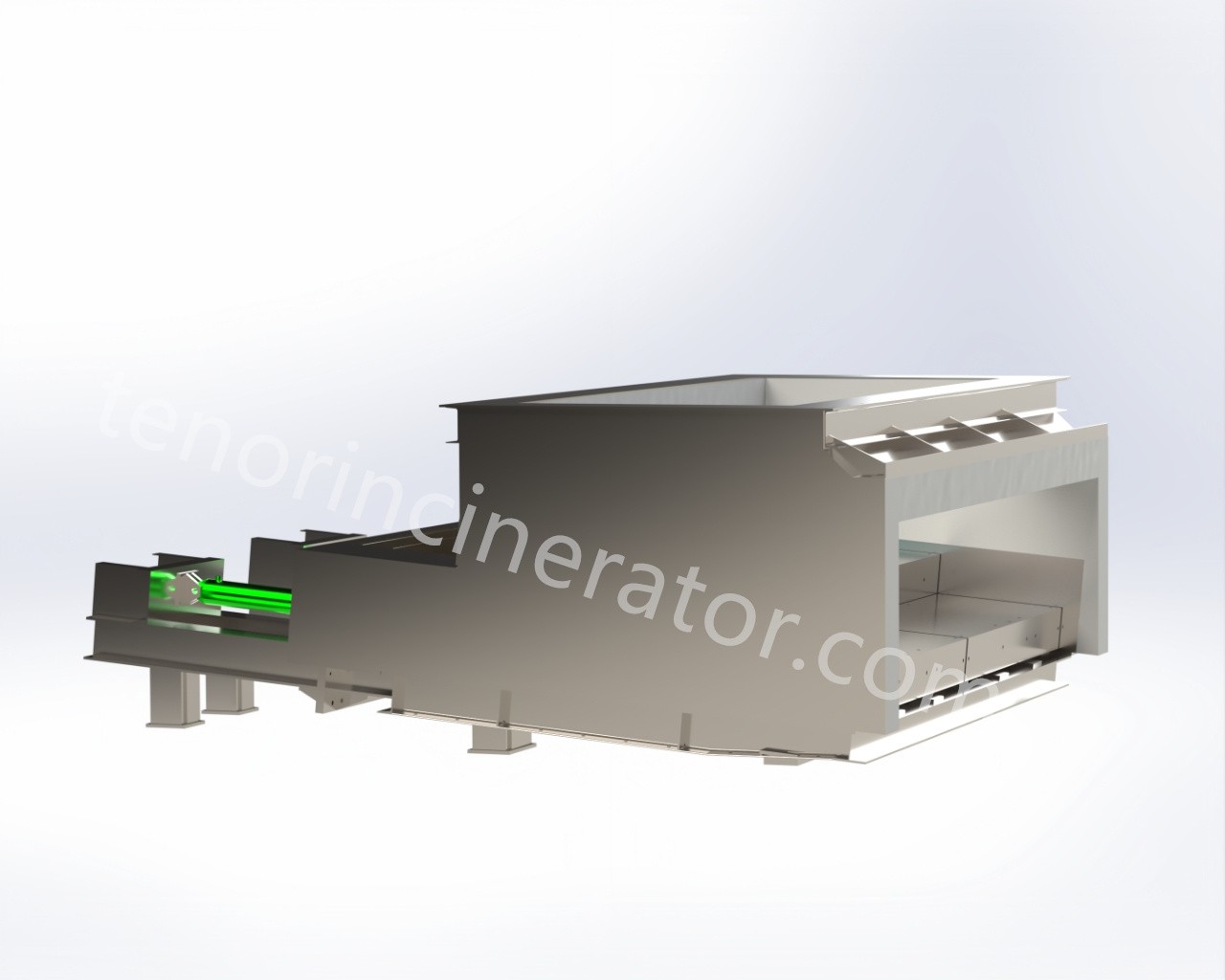
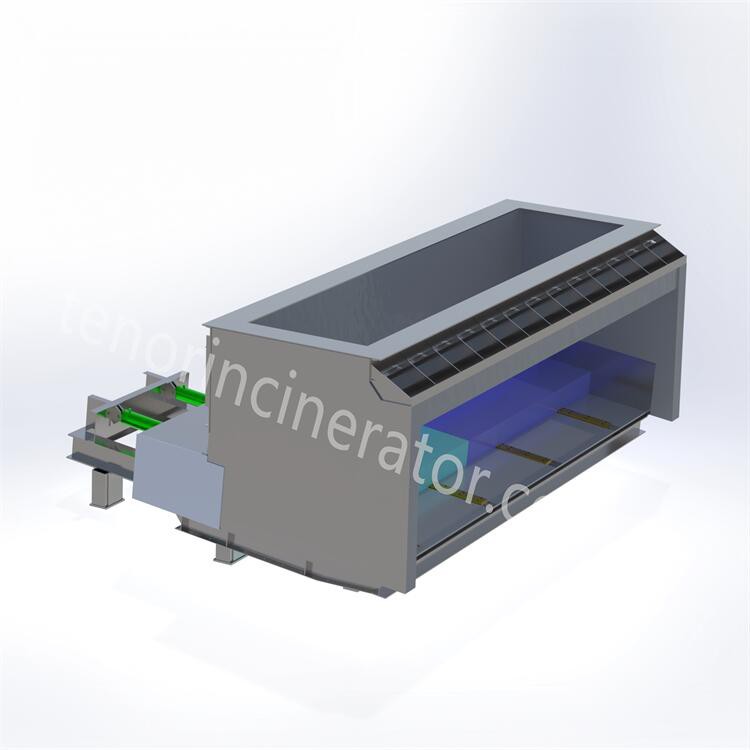
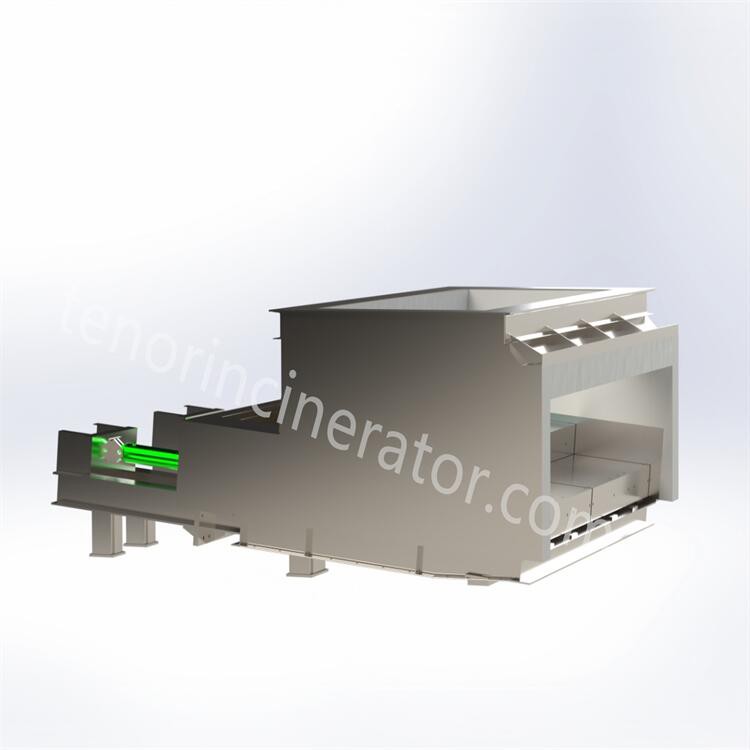
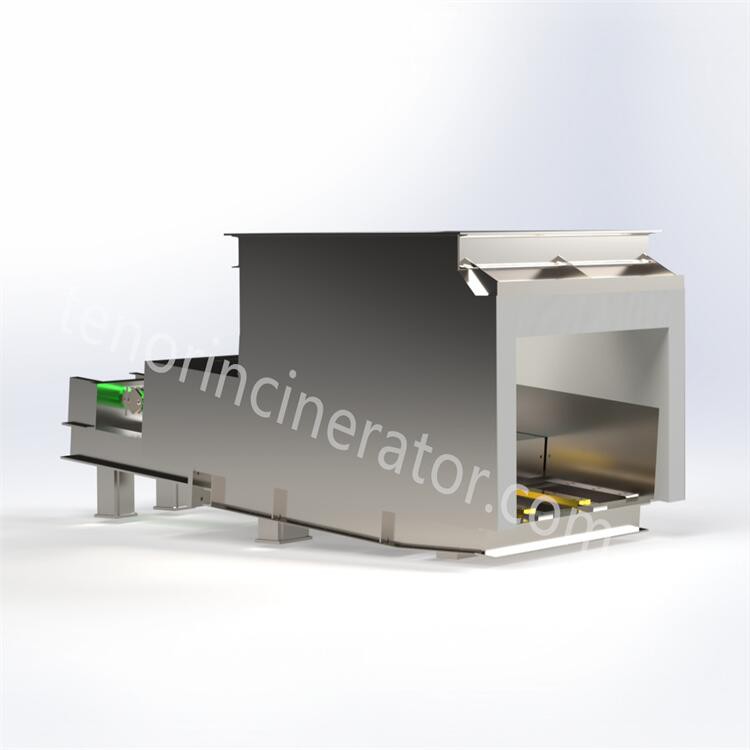
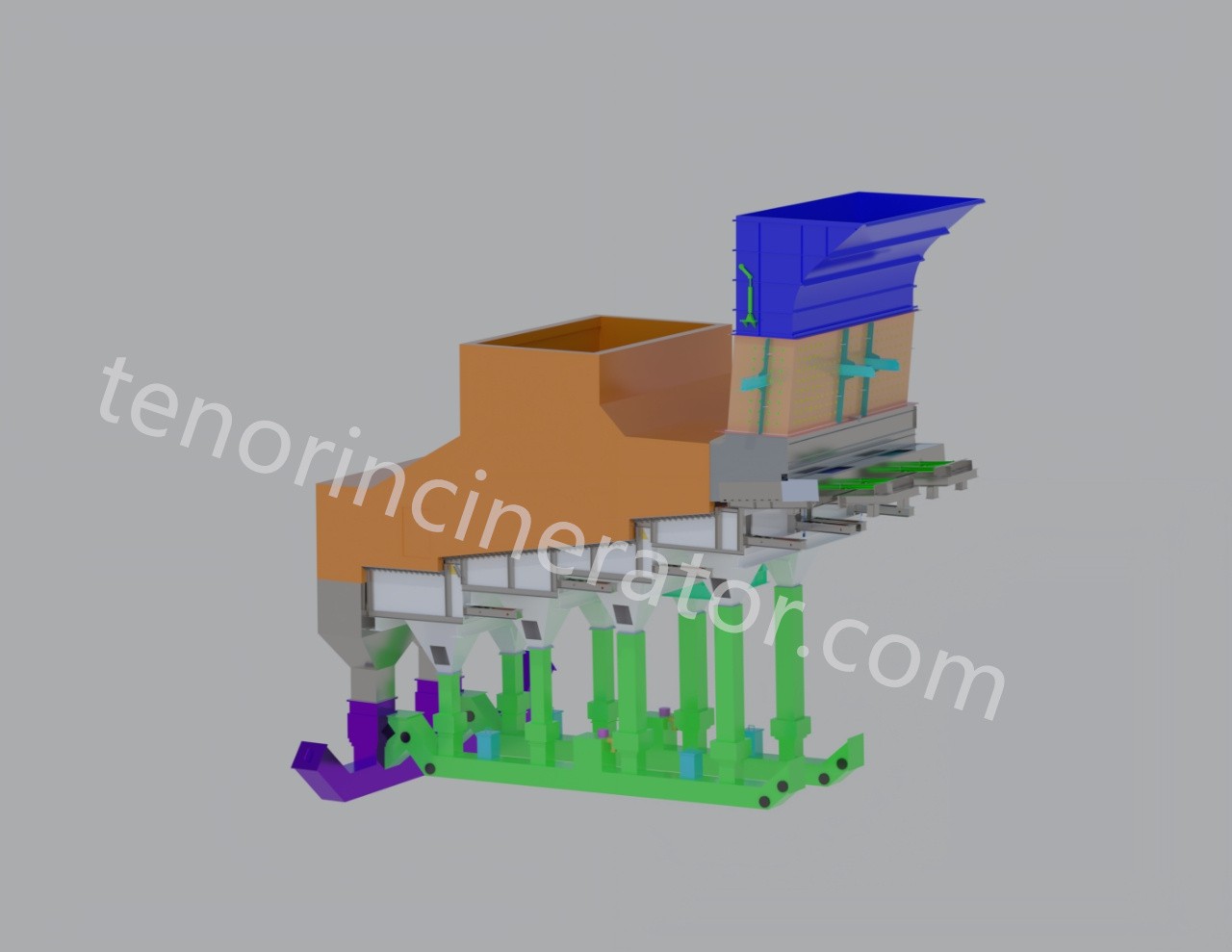
Tenor waste incineration grate is developed by Tenor Low Carbon New Energy Technology (Liaoning) Co., Ltd. The incineration system consists of feeder, grate, ash hopper, ash conveyor and slag remover, and it is suitable for the domestic waste incineration projects with a daily capacity of 30~600 tons.
Why hydraulic pusher is an important equipment in the waste incineration system.
Hydraulic Pusher of the garbage incinerator is an important piece of equipment in the garbage incineration system.
I. Function
1. Pushing garbage: Hydraulic Pusher moves garbage evenly from the feed port into the incinerator for incineration, ensuring continuous and stable entry of garbage to maintain the continuity of the incineration process.
2. Controlling the feeding speed: The pushing speed of garbage can be adjusted according to the operating status and process requirements of the incinerator, thereby controlling the combustion conditions within it.
II. Structural Composition
1. Pusher plate: This part is in direct contact with the garbage and is responsible for pushing it into the incinerator. Hydraulic Pusher plate is typically made of high-temperature and corrosion-resistant materials to withstand the harsh environment of garbage incineration.
2. Drive device: This provides the power for Hydraulic Pusher's operation, generally using hydraulic or mechanical drive systems. The drive device must have sufficient power and reliability to ensure stable operation of Hydraulic Pusher.
3. Guide device: This ensures that Hydraulic Pusher plate maintains the correct direction of movement while pushing garbage, preventing it from deflecting or getting stuck. III. Working Principle Hydraulic Pusher drives the push plate to reciprocate along the track via the drive device, pushing garbage from the feed port into the incinerator. When the push plate moves forward, garbage is pushed into the incinerator; when it moves backward, new garbage falls into the space in front of the push plate, awaiting the next push.
IV. Maintenance
1. Regular inspection: Check the wear of the push plate and replace it if there is significant wear. Also, inspect the operating status of the drive and guide devices to ensure normal operation.
2. Cleaning and maintenance: Regularly clean the garbage and debris around Hydraulic Pusher to prevent interference with its normal operation. Additionally, keep the surface of Hydraulic Pusher clean to prevent corrosion.
3. Lubrication and maintenance: Regularly lubricate the moving parts of Hydraulic Pusher to reduce wear and friction, extending the equipment's service life. Hydraulic Pusher of the garbage incinerator plays a vital role in the garbage incineration process. Its performance and reliability directly affect the operating efficiency and environmental protection effects of the garbage incineration system.




The working status of the pusher in the incinerator can be detected in the following ways:
1. Operation parameter monitoring: - Speed monitoring: Install a speed sensor on the drive device or moving parts of the pusher to measure the push speed in real time. The speed sensor can be a rotary encoder or an electromagnetic speed sensor. Under normal circumstances, the push speed should remain stable within the design range. If the speed becomes abnormally slow, it may be due to garbage blockage, drive device failure, or mechanical component wear; if the speed becomes abnormally fast, it may result from a control system failure or the pusher losing load (e.g., the push plate being disconnected from the garbage). - Displacement monitoring: Monitor the displacement of the pusher's push plate by installing a displacement sensor, such as a linear displacement sensor or a travel switch. This allows for accurate assessment of whether the stroke of each push meets requirements and if the push plate can reach the specified position smoothly. Insufficient displacement may indicate excessive garbage resistance or mechanical jamming, while exceeding the range may signal sensor failure or control system issues. - Thrust monitoring: Use a pressure sensor or force sensor installed on the hydraulic cylinder or push mechanism to monitor the thrust of the pusher. Changes in the composition, humidity, or accumulation of garbage will affect the required thrust. If thrust increases abnormally, it may be due to large hard objects in the garbage or tight packing; if thrust decreases abnormally, it could indicate hydraulic cylinder leakage or reduced drive power.
2. Visual monitoring: - Install cameras: Place high-definition cameras at the feed inlet of the incinerator and the pusher's working area to monitor its operation in real time. Operators can visually observe the push plate's movement, the pushing of garbage, and any foreign objects or blockages through the monitoring screen. This method allows for timely detection of mechanical failures or garbage blockages, though cameras need regular cleaning and maintenance to ensure image quality. - Infrared thermal imaging monitoring: Utilize infrared thermal imaging technology to monitor the pusher. The pusher generates heat during operation, and an infrared thermal imager can detect the temperature distribution of its components. If a part's temperature rises abnormally, it may indicate friction, overload, or potential faults; if the temperature is too low, it may suggest a fault in the heating device or poor contact with the garbage.
3. Sound monitoring: - Microphone monitoring: Install a microphone near the pusher to collect sound signals during operation. A normally operating pusher will emit sound at a certain frequency and intensity. When it fails, the sound may change, producing abnormal noise, vibration, or friction. By analyzing the sound signal, it can be determined whether the pusher is functioning properly. This method can detect potential failures early, but accurate analysis is required to avoid misjudgments.
4. Current monitoring: Install a current sensor on the drive motor or hydraulic system motor to monitor the working current. When the pusher operates normally, the motor current fluctuates within a certain range; if resistance increases or there is mechanical jamming, the current will significantly rise; if the motor fails or the drive system is abnormal, the current may drop or fluctuate unusually. Monitoring and analyzing the current signal can reveal electrical or mechanical failures of the pusher in a timely manner.
5. Regular inspection and maintenance: - Manual inspection: Operators should regularly conduct on-site inspections of the pusher to check its appearance, connection parts, and lubrication conditions. Inspect for push plate deformation, wear, or damage, loose connection bolts, and smooth guide rails. The pusher can also be manually operated to check for flexibility and any jamming. - Shutdown inspection: During incinerator shutdown and maintenance, a full inspection of the pusher should be conducted. This includes disassembling parts, checking the internal mechanical structure, transmission parts, seals, etc., replacing severely worn parts, and maintaining the lubrication system.
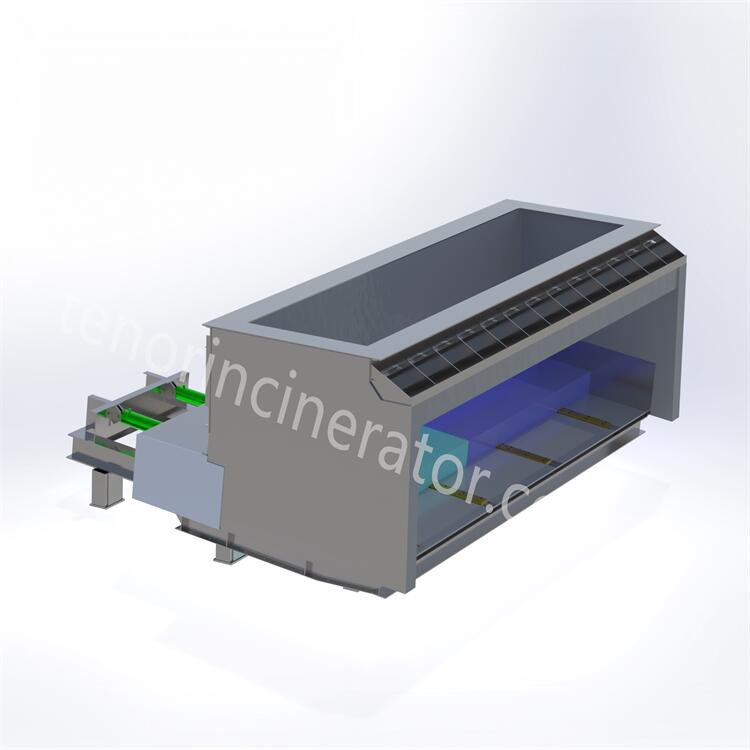
main equipment
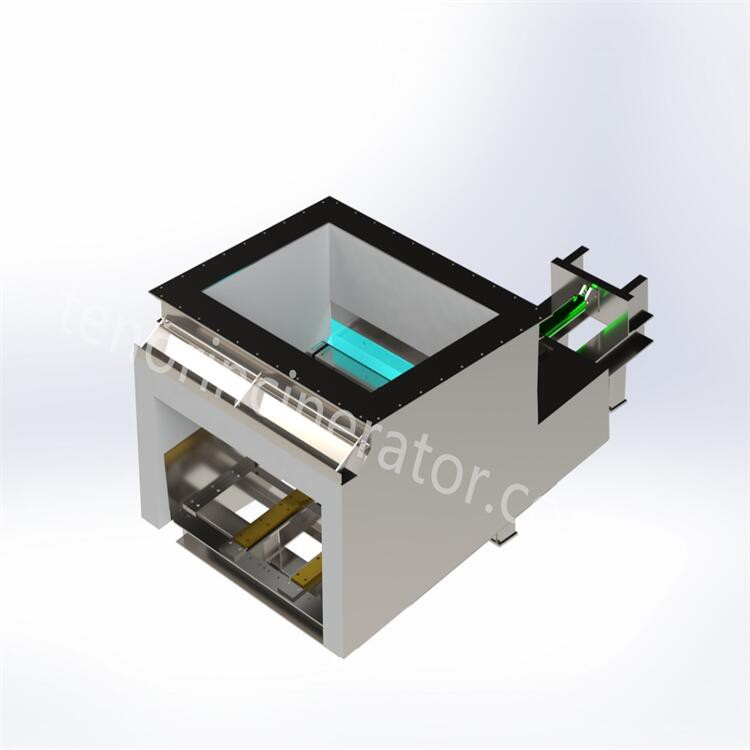
Hopper & feeder
Feeding system consists of hopper and feeder, hopper internal gate, the gate to ensure the sealing at the same time to take into account the function of breaking the bridge, in the garbage clusters bridge blocked hopper through the gate movement to realize the bridge. The feeder and the gate are driven by cylinders to push a certain amount of garbage into the incinerator through periodic reciprocating push and pull movements, and the feeder can adjust the feeding speed according to the load of the incinerator
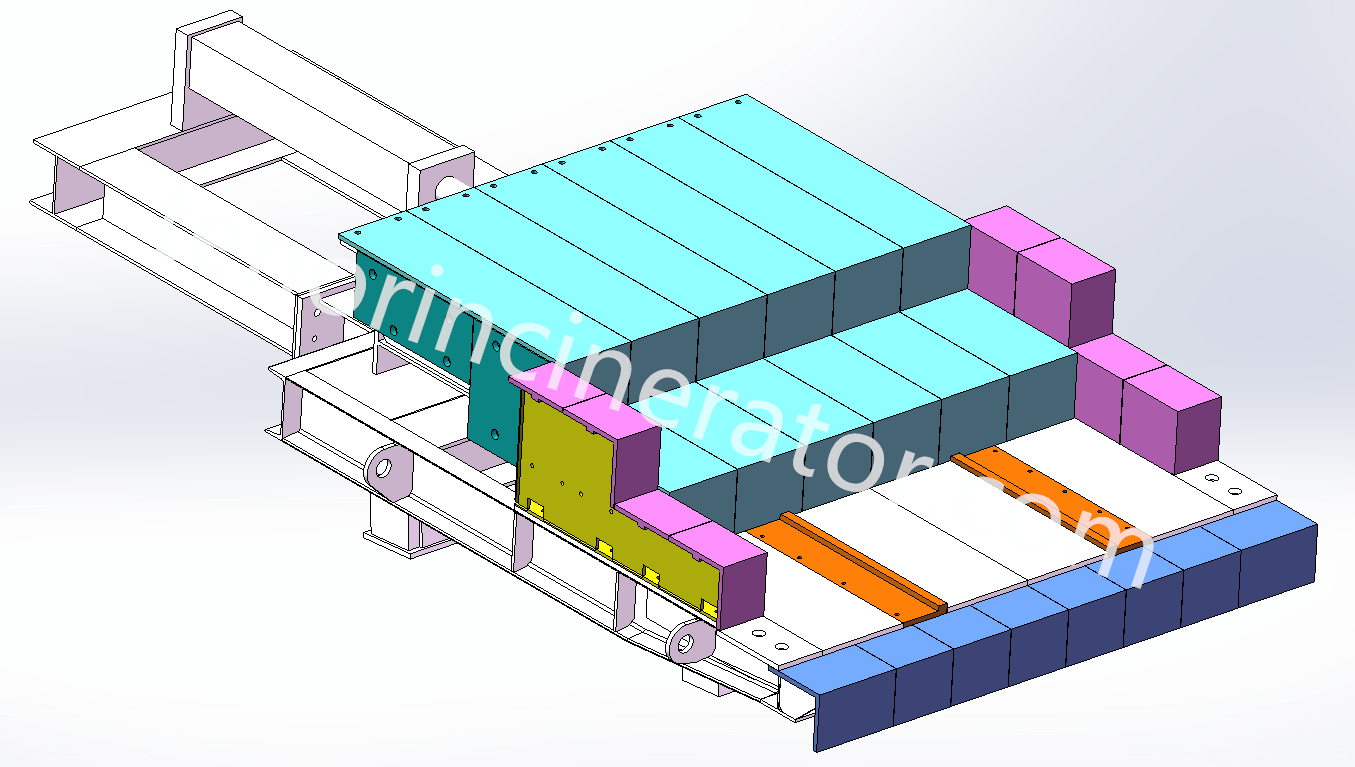
Step Grate
Tenor garbage incineration grate is a downward-pushing stepped inclined reciprocating grate, the grate is divided into three stages of drying, combustion and burning out, and a height difference is set between each section of the grate, so that the garbage is scattered after falling and the garbage is pushed to move, and at the same time the garbage is prevented from gathering together to lead to incomplete combustion. The step grate is driven by hydraulic cylinders, and the three sections of the grate can be controlled independently, so that the movement cycle of the grate can be adjusted according to the combustion state in the furnace. The grate is made of heat-resistant cast steel, which has good wear-resistant, high temperature-resistant and corrosion-resistant properties..

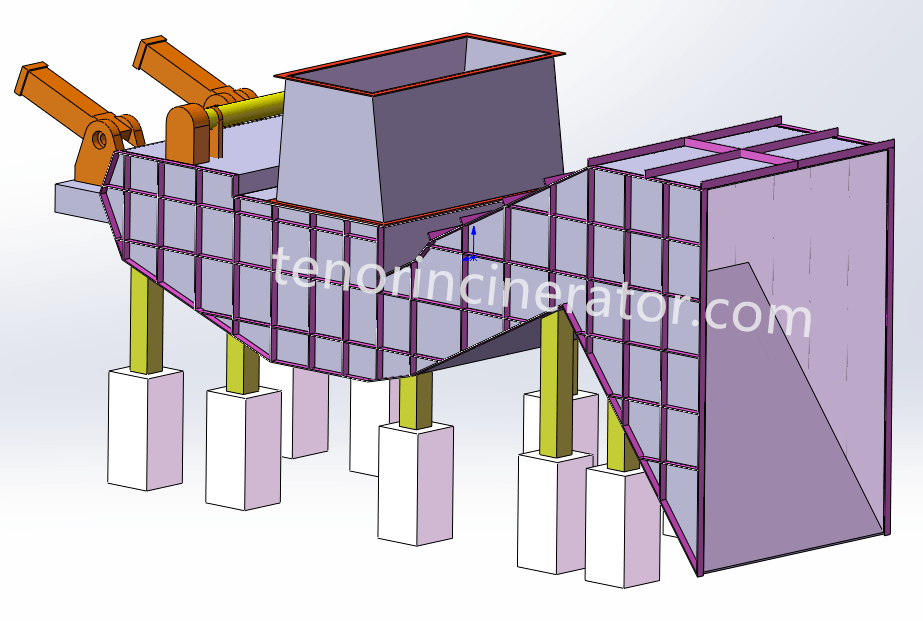
Ash conveyor, slag remover
The ash system consists of an under-furnace ash hopper (cum air chamber), a horizontal ash conveyor, and a slag remover. The small amount of fine ash produced after complete waste combustion falls into the ash hopper through the grate gap and then collects in the horizontal ash conveyor. The main ash produced by waste combustion is pushed into the slag bucket through the grate of the combustion section, and then enters the wet slag remover together with the fine ash. All the ash is sent to
the slag pit by the slag remover.
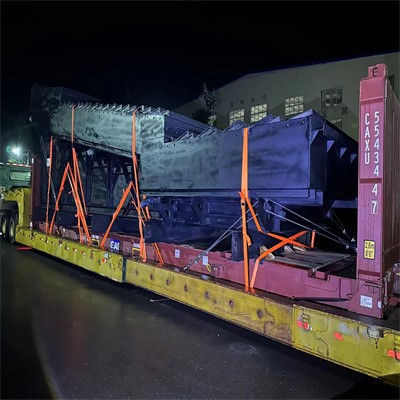
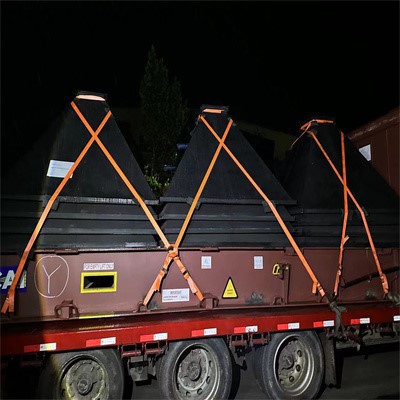
Our Services - Cargo Loading Supervision and Securing












